A seamless procurement cycle not only ensures timely access to goods and services but also contributes significantly to cost savings and overall operational efficiency. At the heart of this intricate process lies a seemingly mundane yet strategically pivotal element: purchase invoices. These unassuming documents hold the power to streamline procurement operations, enhance supplier relationships, and provide data-driven insights for informed decision-making.
Purchase invoices play a multifaceted role in this journey toward procurement excellence. They not only serve as a record of financial transactions but also act as bridges between various stages of the procurement process.
As businesses continue to grow and adapt to technological advancements, the landscape of procurement is evolving rapidly. Automation and digital transformation are redefining traditional procurement processes, with purchase invoices at the forefront of this evolution.
This article delves into the strategic role of purchase invoices in streamlining procurement, highlighting their integration within the procurement cycle, their data-driven decision-making potential, and the ways in which technology is reshaping their management.

By understanding the pivotal role of purchase invoices and embracing innovative solutions, organizations can unlock efficiency gains, foster collaboration, and position themselves at the vanguard of modern procurement practices.
- Brief Overview of Procurement and its Significance in Business Operations
- Introduction to Purchase Invoices and Their Role In the Procurement Process
- Importance of Streamlining Procurement for Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
- The Procurement Process: An Overview
- Steps involved in the procurement process
- Understanding Purchase Invoices
- Strategic Role of Purchase Invoices
- Streamlining Procurement Through Purchase Invoices
- Technology's Role in Invoice Management
- Overcoming Challenges in Invoice Management
- Future Trends in Purchase Invoices and Procurement
- Conclusion
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Brief Overview of Procurement and its Significance in Business Operations
Procurement serves as the pivotal function in an organization's supply chain, encompassing the acquisition of goods, services, and resources required for its operations. This intricate process is not only about acquiring products but involves a series of strategic steps that collectively ensure the timely availability of necessary inputs while optimizing costs and maintaining quality. Procurement's significance in business operations is multifaceted and extends beyond the mere act of purchasing.
Firstly, procurement impacts cost management. It directly influences the organization's expenditure, making it crucial for businesses to make informed decisions regarding sourcing, negotiations, and supplier management. A well-structured procurement strategy can lead to cost savings through bulk purchasing, competitive bidding, and supplier evaluation.
Secondly, procurement affects operational efficiency. Timely acquisition of goods and services is essential to keep production and services on track. Effective procurement processes ensure that there are no delays or disruptions due to inventory shortages or supplier issues.
Thirdly, procurement plays a critical role in quality control and risk management. Selecting reliable suppliers and establishing quality standards helps maintain consistent product or service quality. Mitigating risks such as supply chain disruptions, compliance violations, or vendor-related issues is also an integral part of procurement.
Moreover, procurement contributes to supplier relationship management. Building and nurturing strong relationships with suppliers fosters collaboration, communication, and even innovation. Suppliers can become strategic partners, contributing ideas and insights that drive overall business improvement.
Additionally, in today's globally interconnected business world, procurement also intersects with sustainability and ethical considerations. Organizations are increasingly expected to consider the environmental and social impact of their supply chain decisions. Sustainable sourcing, fair labor practices, and responsible resource utilization are vital aspects of modern procurement practices.
In summary, procurement's significance lies in its role as a nexus for financial efficiency, operational effectiveness, risk mitigation, quality control, and strategic collaboration. Businesses that recognize and optimize the value of procurement are better positioned to navigate competitive landscapes, ensure continuity, and drive sustainable growth.
Introduction to Purchase Invoices and Their Role In the Procurement Process
In the intricate world of procurement, where goods and services traverse from supplier to recipient, purchase invoices emerge as the silent orchestrators of financial transactions. A purchase invoice, often considered a routine administrative document, serves as a crucial thread that weaves through the entire procurement process, ensuring accuracy, transparency, and accountability.
Its role transcends beyond the realm of a mere bill – it acts as a bridge, connecting the dots between supplier agreements, order fulfillment, and financial reconciliation.
Purchase invoices are a formal request for payment, issued by a supplier to a buyer for the products or services delivered. These invoices encapsulate a treasure trove of information – from the specifics of the procurement, such as quantities, prices, and terms, to key identifiers like purchase order numbers and contract details. The intricate dance of procurement is completed when a purchase invoice is processed, verified, and approved, culminating in the release of funds and sealing the deal.
The strategic significance of purchase invoices in the procurement ecosystem cannot be overstated. They serve as tangible evidence of a transaction's completion, validating the goods or services received. More importantly, purchase invoices act as a checkpoint in the procurement journey, enabling organizations to verify whether the terms agreed upon during supplier negotiations align with the actual delivery.
The orchestration of purchase invoices within the procurement process ensures accuracy and accountability. It helps to uncover discrepancies, prevent overpayments, and flag potential issues. Moreover, purchase invoices contribute to supplier relationship management – prompt and accurate processing of invoices fosters positive supplier interactions, leading to smoother transactions and long-term collaboration.
In this era of digital transformation, technology has breathed new life into the world of purchase invoices. Automation, electronic invoicing, and data analytics have propelled this administrative document into a realm of strategic potential. From detecting patterns for cost optimization to enhancing compliance monitoring, purchase invoices have evolved into a source of actionable insights that steer the course of procurement strategy.
Through a deeper understanding of purchase invoices, businesses can unveil opportunities to not only optimize their procurement procedures but also elevate their overall operational excellence.
Importance of Streamlining Procurement for Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
In the fast-paced and competitive business environment of today, the optimization of procurement processes has emerged as a strategic imperative for organizations aiming to thrive. Streamlining procurement isn't merely an operational enhancement; it's a cornerstone that holds the potential to elevate efficiency, drive cost-effectiveness, and ultimately bolster the bottom line.
Operational Efficiency: Procurement involves a series of interconnected steps, from identifying needs and selecting suppliers to processing orders and payments. An unoptimized process can lead to bottlenecks, delays, and inefficiencies that ripple across the entire organization.
Streamlining procurement simplifies these steps, reducing cycle times and minimizing administrative overhead. When purchasing workflows are seamless and well-coordinated, organizations can redirect resources toward core activities, thereby maximizing productivity.
Cost Savings: Procurement inefficiencies often come at a significant cost. Lengthy approval cycles, manual data entry, and communication gaps can all contribute to unnecessary expenditures. By streamlining procurement, organizations can identify opportunities for cost reduction.
Negotiating better terms with suppliers, leveraging bulk purchasing, and minimizing maverick spending become feasible. Furthermore, streamlined procurement processes minimize the risk of errors and double payments, which can lead to financial leakages.
Supplier Relationships: A streamlined procurement process doesn't only benefit the buying organization; it's a win-win for suppliers as well. Predictable orders, prompt payments, and clear communication foster healthier relationships with suppliers.
This, in turn, can lead to improved terms, priority service, and potential collaboration on innovative initiatives. A well-managed procurement process ensures that suppliers remain engaged and motivated to provide high-quality goods and services.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Streamlined procurement processes generate a wealth of data that can be analyzed to extract insights. With accurate and timely data at their fingertips, organizations can make informed decisions. They can identify trends, track supplier performance, and uncover opportunities for strategic sourcing.
Data-driven procurement strategies lead to better allocation of resources, improved risk management, and the ability to adapt quickly to market changes.
Strategic Agility: In a rapidly evolving business landscape, agility is paramount. Organizations that can pivot their procurement strategies swiftly are better equipped to seize opportunities and navigate challenges. Streamlined procurement processes enhance agility by reducing administrative hurdles and facilitating quick decision-making. This flexibility enables organizations to respond to market fluctuations, emerging technologies, and changing customer demands.
In conclusion, streamlining procurement isn't just a matter of convenience; it's a strategic imperative for businesses seeking to optimize their operations, enhance their financial performance, and maintain a competitive edge.
Efficient procurement processes transcend traditional boundaries, enabling organizations to foster better supplier relationships, make data-driven choices, and remain nimble in the face of uncertainty. As the nexus of purchasing activities, streamlined procurement becomes a cornerstone for organizational success in today's dynamic business landscape.
The Procurement Process: An Overview
The procurement process is a structured sequence of steps that organizations follow to acquire goods, services, or resources needed for their operations. This process ensures that the right products are obtained from the right suppliers at the right time and cost. It typically comprises several key stages:
Identification of Needs: The process begins with identifying the organization's requirements, often driven by factors like production demand, project timelines, or inventory levels.
Supplier Selection and Negotiation: Organizations evaluate potential suppliers based on criteria such as quality, price, reliability, and past performance. Negotiations take place to finalize terms, conditions, and pricing agreements.
Purchase Order Issuance: Once a supplier is chosen, a purchase order is generated. This formal document outlines the details of the purchase, including item specifications, quantities, delivery dates, and agreed-upon prices.
Goods or Services Receipt: Upon delivery, the organization verifies that the received goods or services match the purchase order specifications. Any discrepancies or defects are addressed with the supplier.
Invoice Processing and Payment: After successful verification, the supplier submits a purchase invoice requesting payment. The invoice is checked for accuracy and compliance with contractual terms before payment is authorized.
These stages, when executed cohesively, ensure a smooth flow of resources into the organization, facilitating operations while maintaining cost-efficiency and supplier relationships.
Steps involved in the procurement process
The procurement process is a strategic framework that guides organizations in acquiring goods, services, or resources necessary for their operations. It typically consists of the following key steps:
1. Identifying procurement needs
This stage involves assessing the organization's requirements. Factors such as project demands, inventory levels, and operational goals dictate what needs to be procured. Clear understanding of these needs forms the foundation for the subsequent steps.
This initial step involves understanding the organization's operational and project-based requirements. This can be driven by production schedules, inventory depletion, or specific project needs. Accurate identification of needs is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire procurement process.
2. Supplier selection and negotiation
Once the needs are clear, organizations research and evaluate potential suppliers. Factors like quality, reliability, cost, and track record are considered. Negotiations come into play to establish terms that are favorable for both parties, ensuring mutual benefit and a sustainable partnership.
3. Purchase order issuance
With supplier selection and negotiation concluded, a purchase order is generated. This document outlines the specifics of the transaction, including what is being purchased, quantities, prices, delivery timelines, and any other relevant terms. The purchase order formalizes the agreement between the organization and the supplier.
4. Goods or services receipt
When the supplier delivers the goods or completes the services, the organization inspects the received items. This step ensures that the delivered goods match the specifications in the purchase order. Any discrepancies or defects are addressed with the supplier to ensure alignment with expectations.
5. Invoice processing and payment
Upon successful verification of the received items, the supplier submits an invoice for payment. The invoice is carefully reviewed to ensure accuracy, proper documentation, and compliance with the terms outlined in the purchase order. After approval, payment is processed, completing the procurement cycle.
These steps collectively form a cohesive and systematic approach to procurement, enabling organizations to meet their operational needs efficiently while maintaining supplier relationships and financial integrity.
Understanding Purchase Invoices
As transactions and negotiations intertwine, purchase invoices emerge as the financial compass guiding organizations through the intricate landscape of supplier interactions.
These unassuming documents hold within them a wealth of information that transcends mere billing – they encapsulate the essence of transactions, serving as crucial checkpoints that validate the alignment between expectations and reality. To truly comprehend their strategic significance, it is essential to delve deeper into the components, purpose, and intricacies that define purchase invoices within the procurement ecosystem.
This section unveils the layers of purchase invoices, revealing how they not only document transactions but play a pivotal role in fostering transparency, accuracy, and accountability throughout the procurement process.
A. Definition and purpose of purchase invoices
Purchase invoices, often referred to as supplier invoices or vendor bills, are formal documents issued by suppliers to buyers to request payment for goods delivered or services rendered. These documents serve as a vital bridge between the completion of a transaction and the subsequent financial settlement.
Definition: A purchase invoice is a written statement that outlines the details of a commercial transaction between a supplier and a buyer. It provides a breakdown of the items or services provided, their quantities, unit prices, and the total amount due from the buyer to the supplier. Additionally, it includes essential identifiers such as purchase order numbers, delivery dates, and terms of payment.
Purpose: The primary purpose of purchase invoices is to facilitate smooth and accurate financial transactions between parties engaged in business. They offer a formal record that validates the completion of obligations – from fulfilling orders to delivering goods. Purchase invoices also play a critical role in documenting the terms and conditions agreed upon during negotiations, ensuring that both parties honor their commitments.
Beyond financial transactions, purchase invoices are integral to various aspects of procurement management:
Verification and Reconciliation: Purchase invoices allow buyers to verify that the delivered goods or services align with the agreed-upon terms and quantities in the purchase order. This verification helps prevent discrepancies, errors, and potential disputes.
Supplier Relationships: Timely and accurate processing of purchase invoices contributes to positive supplier relationships. Efficient handling of invoices demonstrates reliability and professionalism, fostering trust between buyers and suppliers.
Financial Accountability: Purchase invoices form a crucial part of a company's financial records. They provide transparency in the organization's financial obligations, aiding in budgeting, auditing, and financial reporting.
Compliance and Audit Trail: Purchase invoices contribute to regulatory compliance by documenting transactions for tax and financial reporting purposes. They also create an audit trail that can be traced back for verification or analysis.
In essence, purchase invoices are the tangible evidence of completed transactions, anchoring the financial dimension of procurement processes. Their accurate processing, verification, and management are essential for maintaining healthy supplier relationships, financial transparency, and efficient operations
B. Components of a typical purchase invoice
A typical purchase invoice is a comprehensive document that encompasses several crucial components, each serving a specific purpose to facilitate accurate transactions and clear communication between buyers and suppliers. These components provide a detailed snapshot of the transaction, ensuring transparency, accountability, and compliance.
Supplier Information: This section includes details about the supplier, such as the legal name of the company, contact information (address, phone number, email), and possibly tax identification numbers or other regulatory identifiers. Supplier information is vital for accurate record-keeping and for initiating payments.
Purchase Order Details: The purchase order (PO) number, along with the associated date, is often included on the invoice. This links the invoice to the original purchase order, allowing buyers and suppliers to easily reference the terms, quantities, and agreed-upon prices.
Itemized List of Products/Services: This section provides a breakdown of the goods delivered or services rendered. Each item is listed individually, along with a brief description that aids in identifying the nature of the product or service. This level of detail is crucial for verification against the purchase order and receipt of goods.
Quantities, Prices, and Total Amounts: The itemized list is accompanied by the quantities of each item delivered, unit prices, and extended amounts (quantity multiplied by price). These values provide a clear understanding of the financial aspects of the transaction and contribute to the calculation of the total invoice amount.
Terms of Payment and Due Date: Here, the agreed-upon terms of payment are outlined. This includes the due date by which the payment should be made. Additionally, any early payment discounts or late payment penalties may be specified in this section. Clearly defined terms of payment help both parties understand their obligations and avoid misunderstandings.
In essence, the meticulous inclusion of these components in a purchase invoice fosters transparency, simplifies reconciliation, and enables smooth communication between buyers and suppliers, contributing to efficient and accurate financial transactions.
Strategic Role of Purchase Invoices
Within the intricate realm of procurement, purchase invoices emerge as more than mere financial records; they are powerful tools that wield a profound impact on organizational strategies. These unassuming documents play a pivotal role in streamlining processes, safeguarding financial integrity, and unlocking a treasure trove of data-driven insights.
As organizations increasingly seek to optimize operations and bolster supplier relationships, understanding the strategic significance of purchase invoices becomes paramount. This section delves into the multifaceted role that purchase invoices play in shaping procurement strategies, illuminating their integration within procurement cycles, their potential to drive compliance and risk management, and their transformation into sources of invaluable intelligence for informed decision-making.
By unveiling the strategic layers of purchase invoices, organizations can harness their potential to navigate the complexities of procurement with enhanced efficiency and foresight.
A. Integration with procurement process
The integration of purchase invoices within the procurement process is akin to a finely tuned orchestra, harmonizing various stages of transactional flow to ensure accuracy, transparency, and efficiency. This integration facilitates a seamless transition from the initiation of a purchase to the final financial settlement, allowing organizations to navigate procurement complexities with precision.
It involves the strategic alignment of purchase orders, goods or services receipt, and supplier invoicing to create a synchronized ecosystem.
Linking Purchase Orders and Invoices for Accurate Reconciliation: At the heart of procurement integration lies the linkage between purchase orders and purchase invoices. A purchase order serves as a blueprint for a transaction, specifying the terms, quantities, and agreed-upon prices. When the purchase invoice arrives, it provides a detailed account of the actual goods or services delivered, along with their respective costs.
By cross-referencing the purchase order with the invoice, organizations can accurately reconcile the planned transaction with the executed one. This process minimizes discrepancies and errors, creating a transparent audit trail that ensures financial accuracy.
Avoiding Duplicate Payments through Cross-Referencing: Duplicate payments can be detrimental to an organization's financial health. The integration of purchase orders and invoices allows organizations to cross-reference records to prevent inadvertent duplicate payments.
When invoices are received, they can be matched against purchase order records and previous payment history to ensure that the same transaction isn't paid for multiple times. This cross-referencing mechanism acts as a safeguard against errors and ensures that financial resources are allocated appropriately.
In essence, the integration of purchase invoices with the procurement process ensures a coherent and synchronized flow of transactions, minimizing errors, enhancing financial accuracy, and fostering efficient reconciliation. By establishing a seamless connection between purchase orders and invoices, organizations not only ensure compliance with terms and agreements but also lay the foundation for informed decision-making and robust supplier relationships.
B. Data-driven insights for decision-making
In the modern business landscape, where informed decision-making reigns supreme, purchase invoices have evolved from mere financial records to invaluable sources of data-driven insights. Leveraging the data contained within these documents empowers organizations to make informed choices that optimize procurement strategies, enhance supplier relationships, and drive overall operational efficiency.
Analyzing Invoice Data for Supplier Performance Evaluation: Beyond the financial transaction itself, invoices provide a trail of interaction between buyers and suppliers. This includes delivery times, order accuracy, and responsiveness to queries or issues.
By systematically analyzing this data, organizations can objectively evaluate suppliers based on their performance metrics. This evaluation forms the basis for supplier relationship management, helping organizations collaborate with high-performing suppliers and address issues with underperforming ones.
Identifying Cost-Saving Opportunities through Spend Analysis: Invoice data contains a comprehensive breakdown of expenses incurred. When aggregated and analyzed, this data can reveal spending patterns, vendor preferences, and opportunities for optimization. For instance, identifying suppliers offering the best value for specific products can lead to strategic sourcing decisions.
Furthermore, understanding peak spending periods can aid in negotiating bulk discounts. This data-driven approach to spend analysis enhances cost control and supports more efficient procurement practices.
In summary, purchase invoices have transcended their traditional role as financial documents to become powerful tools for data-driven decision-making. By extracting insights from invoice data, organizations can evaluate suppliers objectively, identify areas for cost reduction, and fine-tune procurement strategies for enhanced efficiency and strategic growth.
C. Compliance and risk management
In the intricate landscape of procurement, compliance and risk management emerge as critical pillars for maintaining operational integrity and financial transparency. Purchase invoices play a central role in these areas, serving as a mechanism to ensure adherence to contractual agreements, safeguard against discrepancies, and mitigate potential instances of fraud.
Ensuring Adherence to Contractual Terms and Pricing Agreements: Contracts form the foundation of business relationships, outlining the terms, conditions, and pricing agreements between buyers and suppliers. Purchase invoices act as a touchstone for compliance, providing a tangible record against which organizations can verify that the terms specified in the contract are being honored.
By meticulously cross-referencing purchase orders, delivery receipts, and invoices, organizations can identify deviations from agreed-upon terms and address them promptly.
Mitigating Fraud and Discrepancies through Invoice Verification: Fraudulent activities or unintentional errors can infiltrate even the most robust procurement processes. Purchase invoice verification acts as a safeguard against these threats. By rigorously reviewing and validating each invoice against corresponding purchase orders and delivery receipts, organizations can detect discrepancies early.
This process helps prevent overbilling, double payments, and fraudulent invoicing, reducing the risk of financial loss and reputational damage.
In conclusion, purchase invoices serve as powerful tools for compliance and risk management in procurement. Their integration within the procurement process facilitates adherence to contractual terms, ensuring transparency and accountability. Rigorous verification of invoices against supporting documents mitigates the risk of fraud and discrepancies, safeguarding both financial integrity and organizational reputation.
By diligently managing compliance and risk through purchase invoices, organizations can navigate the complex procurement landscape with confidence and resilience.
Streamlining Procurement Through Purchase Invoices
In the pursuit of operational excellence, organizations continuously seek avenues to optimize their procurement processes. Among the array of tools available, purchase invoices emerge as a linchpin in the quest for streamlined operations. This section explores how purchase invoices, often considered routine administrative documents, hold the potential to revolutionize procurement practices.
By weaving together the intricate threads of accuracy, transparency, and data-driven insights, purchase invoices serve as catalysts for enhanced efficiency, fortified supplier relationships, and well-informed decision-making.
Delving into the strategic integration, compliance enforcement, and risk mitigation facilitated by purchase invoices, this section unveils their transformative power in creating a seamless procurement ecosystem that resonates with precision and purpose.
A. Automation of invoice processing
In the age of technological advancement, the automation of invoice processing stands as a beacon of efficiency and accuracy within the procurement landscape. Automated systems have revolutionized the way organizations handle purchase invoices, minimizing manual interventions, streamlining workflows, and elevating overall operational effectiveness.
Implementing Electronic Invoicing (E-Invoicing) Systems: E-invoicing represents a paradigm shift in invoice processing. Instead of relying on paper-based documents, electronic invoices are digitally generated, transmitted, and received. E-invoicing systems facilitate direct integration between a supplier's invoicing software and the buyer's procurement or accounting systems.
This seamless electronic exchange not only expedites invoice delivery but also significantly reduces the risk of errors, as data is captured electronically and transmitted accurately.
Reducing Manual Data Entry and Errors: Manual data entry is a breeding ground for errors and inefficiencies. Automated invoice processing systems drastically reduce the need for manual data input. E-invoices, for instance, can be directly imported into an organization's systems, minimizing the risk of transcription errors and saving time.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology can also be employed to extract data from scanned paper invoices, further minimizing manual intervention and enhancing accuracy.
In conclusion, the automation of invoice processing, particularly through electronic invoicing systems, represents a transformational leap toward greater efficiency and accuracy in procurement operations. By reducing manual interventions, eliminating errors, and expediting workflows, automated systems reshape the procurement landscape, empowering organizations to embrace a future where streamlined processes are the norm, not the exception.
B. Approval workflows and efficiency
In the intricate dance of procurement, where accuracy and timeliness are paramount, approval workflows emerge as a dynamic force that propels efficiency to new heights. These structured pathways, guided by technological solutions and strategic design, orchestrate the approval process for purchase invoices, ensuring that the right stakeholders provide their authorization promptly and seamlessly.
By integrating approval workflows, organizations not only expedite transactions but also cultivate accountability, transparency, and a culture of informed decision-making.
Approval workflows encompass a series of steps, each assigned to specific individuals or roles within the organization. These steps often include verification of invoice accuracy, confirmation of adherence to contractual terms, and compliance with internal financial controls.
The integration of technology further accelerates these workflows, allowing approvals to be tracked, monitored, and executed digitally. This digital transformation offers a host of benefits:
Enhanced Speed: Automation expedites the flow of invoices through the approval chain. By digitally routing invoices to the appropriate stakeholders, delays associated with physical paper-based routing are eliminated, accelerating the overall process.
Accuracy and Consistency: Automated approval workflows ensure that each invoice is routed to the right individuals for validation. This not only maintains accuracy but also ensures that consistent approval protocols are followed across the organization.
Real-time Monitoring: Technology-enabled workflows provide real-time visibility into the approval status of each invoice. This transparency enables stakeholders to track progress, anticipate bottlenecks, and take proactive measures to keep processes on track.
Data-Driven Insights: Automated workflows generate data that can be analyzed to identify patterns, streamline processes, and optimize approval chains. This data-driven approach enhances decision-making by providing insights into approval times, frequent points of contention, and potential areas for improvement.
By infusing approval workflows with technological prowess, organizations foster efficiency while nurturing a culture of accountability and compliance. The orchestration of approvals becomes a strategic instrument that harmonizes the complexities of procurement, resulting in more streamlined operations, improved supplier relationships, and a heightened capacity to allocate resources effectively.
C. Enhanced collaboration with suppliers
In the realm of modern procurement, the dynamics between buyers and suppliers have evolved beyond transactional interactions to encompass collaborative partnerships. Purchase invoices, often viewed as administrative documents, hold the potential to be transformational tools that nurture and fortify these supplier relationships. By leveraging purchase invoices as touchpoints for communication, transparency, and mutual growth, organizations can elevate their procurement practices to new heights of efficiency and strategic alignment.
Enhanced collaboration with suppliers through purchase invoices involves:
Timely Communication: Purchase invoices facilitate timely communication between buyers and suppliers. By promptly submitting accurate invoices, suppliers demonstrate professionalism and commitment to the partnership. On the buyer's end, efficient processing and payment of invoices indicate reliability and respect for the supplier's contribution.
Transparency and Dispute Resolution: Detailed purchase invoices provide transparency into the specifics of each transaction. This transparency not only reduces the potential for disputes but also facilitates quicker resolution if discrepancies arise. Both parties can refer to the invoice details to clarify any misunderstandings.
Shared Insights: Purchase invoices contain valuable data that, when analyzed, can offer insights into spending patterns, order frequencies, and performance metrics. Sharing these insights with suppliers fosters a collaborative atmosphere, enabling discussions on optimizing orders, enhancing efficiencies, and exploring joint opportunities.
Mutual Growth: Collaborative supplier relationships are a cornerstone of sustainable business growth. Utilizing purchase invoices as a conduit for dialogue allows buyers and suppliers to align their objectives, explore innovative solutions, and jointly address challenges, paving the way for mutual growth.
Process Efficiency: Streamlined invoicing processes benefit both parties. Efficient handling of invoices reduces administrative burdens and enables resources to be channeled into value-added activities. Suppliers, in turn, benefit from timely payments that maintain their financial stability.
By recognizing purchase invoices as more than financial records and instead as instruments for collaboration, organizations can create an ecosystem where buyers and suppliers operate as partners, striving toward shared success. This approach transcends transactional efficiency, elevating procurement into a realm of strategic advantage where collaboration becomes a driving force for innovation and long-term prosperity.
Technology's Role in Invoice Management
As the modern business landscape becomes increasingly intertwined with technological advancements, the realm of invoice management has undergone a revolutionary transformation. Technology has emerged as a powerful catalyst, redefining how organizations handle purchase invoices and altering the very fabric of procurement processes.
This section delves into the intricate dance between technology and invoice management, uncovering how automation, digitization, and advanced tools reshape the landscape of procurement. From electronic invoicing systems that accelerate workflows to data analytics that unveil hidden insights, this section explores the myriad ways in which technology propels efficiency, transparency, and strategic decision-making within the realm of procurement and purchase invoices.
A. Invoice management software
In the digital age, where efficiency and accuracy reign supreme, the emergence of invoice management software stands as a testament to the transformative power of technology within procurement. This sophisticated breed of software solutions has revolutionized the way organizations handle purchase invoices, transcending manual processes and propelling operations into a realm of streamlined workflows, reduced errors, and data-driven insights.
Invoice management software encompasses a diverse array of tools and platforms designed to automate, streamline, and optimize the entire lifecycle of purchase invoices. From receipt and data extraction to verification, approval, and payment, these software solutions orchestrate each stage with precision and speed.
Key features of invoice management software include:
Electronic Invoicing (E-Invoicing): Modern software facilitates the creation, transmission, and receipt of electronic invoices, transforming traditional paper-based processes into seamless digital exchanges. This not only expedites transactions but also reduces the risk of errors associated with manual data entry.
Automated Data Extraction: Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology is often integrated into invoice management software to automatically extract key data from scanned or digital invoices. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and significantly enhances accuracy.
Workflow Automation: Invoice management software streamlines approval workflows, ensuring that invoices are routed to the right stakeholders for validation. Automated workflows reduce processing times, minimize bottlenecks, and enhance accountability.
Document Storage and Retrieval: Software solutions often include centralized repositories where invoices are stored electronically. This digital archive facilitates easy retrieval, audit compliance, and reduces physical storage requirements.
Data Analytics: Advanced software platforms offer data analytics capabilities, allowing organizations to derive insights from invoice data. Spending patterns, supplier performance metrics, and optimization opportunities can be identified to drive informed decision-making.
Integration with ERP Systems: Many invoice management solutions seamlessly integrate with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, enabling a smooth exchange of financial data and enhancing overall financial visibility.
Security and Compliance: Invoice management software prioritizes data security and compliance, offering encryption, authentication, and audit trails to ensure sensitive financial information remains protected.
In conclusion, invoice management software exemplifies the synergy between technology and procurement. By automating processes, reducing errors, and providing data-driven insights, these solutions empower organizations to navigate the complexities of purchase invoices with unprecedented precision and efficiency.
In an era where speed, accuracy, and strategic advantage define success, invoice management software emerges as an indispensable tool within the modern procurement landscape.
B. Data analytics and insights
In the digital age, data has transformed from a mere byproduct of business transactions into a goldmine of insights that organizations can harness to drive strategic decisions. Within the realm of invoice management, data analytics emerges as a powerful tool that not only optimizes processes but also unveils hidden patterns, opportunities, and efficiencies.
Data analytics within invoice management involves:
Spending Analysis: By aggregating and analyzing invoice data, organizations can gain a comprehensive view of their spending patterns. This analysis enables them to identify which categories, suppliers, or products contribute significantly to expenditures, paving the way for targeted cost-saving strategies.
Supplier Performance Metrics: Invoice data offers insights into supplier performance. Organizations can evaluate factors such as on-time delivery, accuracy of invoicing, and responsiveness to issues. These metrics enable informed supplier relationship management and negotiation strategies.
Process Bottlenecks: Analytics can reveal bottlenecks and inefficiencies within the invoice management process. Identifying points of delay or errors helps organizations streamline workflows, reduce processing times, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Early Payment Discounts: Invoice data analytics can uncover opportunities to take advantage of early payment discounts offered by suppliers. By identifying invoices eligible for such discounts and strategically managing payment schedules, organizations can optimize cash flow.
Predictive Insights: Advanced analytics can predict future spending trends based on historical invoice data. This foresight enables organizations to plan budgets, allocate resources, and make informed decisions aligned with future procurement needs.
Fraud Detection: Analytics can flag anomalies in invoice data that may indicate fraudulent activities, such as duplicate invoices or unexpected price changes. This proactive approach safeguards against financial loss and reputational damage.
Process Optimization: By analyzing data, organizations can fine-tune their invoice management processes. This optimization leads to increased accuracy, reduced processing times, and enhanced compliance with financial controls.
In summary, data analytics within invoice management transcends mere analysis; it empowers organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights. These insights steer strategic decision-making, elevate operational efficiency, and foster a culture of informed procurement practices. As organizations continue to harness the power of data, analytics becomes a cornerstone of competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
Overcoming Challenges in Invoice Management
In the pursuit of seamless procurement operations, organizations often encounter a spectrum of challenges within the realm of invoice management. From manual errors and processing delays to compliance hurdles and data security concerns, these challenges can cast shadows over even the most well-structured processes. However, it is within the crucible of these challenges that innovation and strategic solutions emerge.
This section delves into the multifaceted landscape of overcoming challenges in invoice management, exploring how organizations can navigate complexities, fortify their processes, and propel towards operational excellence. By unveiling strategies to address each obstacle head-on, this section equips organizations with the tools to transform challenges into opportunities for growth, efficiency, and precision within their procurement endeavors.
A. Complex invoice formats and data extraction
One of the persistent challenges organizations face is the diverse array of complex invoice formats. These formats, often varying between suppliers and industries, can complicate the process of extracting crucial data accurately. However, technology and automation have risen to the occasion, offering solutions that tame complexity and enhance data extraction precision.
Navigating complex invoice formats and data extraction involves:
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) Technology: OCR technology serves as a powerful ally in deciphering complex invoice formats. This technology converts scanned or digital invoices into machine-readable text, enabling software to extract key data points such as invoice numbers, dates, line items, and monetary values.
Template-Based Data Extraction: Advanced invoice management solutions offer template-based extraction. By training the software to recognize specific invoice layouts, fields, and structures, organizations can automate data extraction with a higher degree of accuracy.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: Machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence can adapt and learn from various invoice formats over time. This enables software to recognize and extract data from new and evolving formats, gradually improving accuracy.
Customization and Validation: Some software solutions allow for manual validation and customization. Users can review extracted data and adjust inaccuracies, training the software for future recognition.
Supplier Collaboration: Collaborative approaches involve working closely with suppliers to standardize invoice formats or data fields. This cooperation streamlines data extraction and benefits both parties.
Supplier Portal Integration: Supplier portals allow suppliers to input invoice data directly into the buyer's system, reducing data extraction complexities and potential errors.
By harnessing automation and innovative technologies, organizations can navigate the intricacies of complex invoice formats and data extraction with greater precision and efficiency. This approach not only minimizes errors but also unlocks the potential to streamline processes, accelerate workflows, and create a foundation for informed decision-making within the realm of procurement.
B. Handling exceptions and discrepancies
In the intricate web of invoice management, the occurrence of exceptions and discrepancies stands as a formidable challenge that demands strategic solutions. These anomalies, ranging from pricing discrepancies to missing information, can disrupt workflows and compromise the accuracy of financial records. However, organizations can fortify their processes and bolster transparency by implementing resilient strategies to address and resolve such challenges.
Overcoming challenges related to exceptions and discrepancies involves:
Automated Exception Handling: Invoice management systems equipped with automated exception handling mechanisms can swiftly identify deviations from the norm. When an exception is detected, the system triggers alerts to appropriate stakeholders, initiating prompt resolution.
Defined Approval Hierarchies: Establishing clear approval hierarchies ensures that discrepancies are escalated to the right individuals for resolution. Having designated decision-makers expedites the process and minimizes delays.
Collaborative Communication: Anomalies often require collaboration between procurement, finance, and supplier teams. Streamlining communication channels and creating a platform for discussion and resolution ensures that exceptions are addressed efficiently.
Document Attachments: Invoice management systems that allow attachments can facilitate the inclusion of supporting documents to explain discrepancies. These attachments enhance transparency and aid in efficient resolution.
Auditing and Reporting: Maintaining a robust audit trail and generating reports on exceptions and their resolutions provides insights into recurring issues. This data-driven approach enables organizations to proactively identify areas for process improvement.
Supplier Collaboration: Open lines of communication with suppliers are crucial when handling discrepancies. Collaborative discussions can lead to swift resolutions and the implementation of preventive measures to avoid similar issues in the future.
Root Cause Analysis: After resolving discrepancies, organizations should conduct root cause analyses to identify underlying issues. This analysis informs process improvements to prevent future anomalies.
By adopting a proactive and strategic approach to handling exceptions and discrepancies, organizations can ensure precision, transparency, and accountability in their invoice management processes. Resilient strategies not only address challenges promptly but also transform them into opportunities for process enhancement, fostering stronger supplier relationships and cultivating a culture of continuous improvement within the realm of procurement.
C. Ensuring data security and compliance
The handling of sensitive financial information, coupled with the ever-evolving landscape of regulatory requirements, demands robust strategies to ensure the protection of data and adherence to industry standards. Organizations can navigate this challenge by implementing comprehensive measures that safeguard data integrity, fortify compliance, and foster trust within their procurement processes.
Addressing data security and compliance involves:
Secure Data Transmission: Utilizing encrypted channels for the transmission of invoices and related information ensures that sensitive data remains confidential during transit.
Access Controls and Permissions: Implementing strict access controls ensures that only authorized personnel can view or interact with sensitive invoice data. Role-based permissions limit access to individuals who require the information for their responsibilities.
Data Encryption: Encrypting stored invoice data safeguards against unauthorized access, even if the data is breached. Encryption transforms the data into an unreadable format without the appropriate decryption key.
Regular Security Audits: Conducting routine security audits evaluates vulnerabilities in the invoice management process. These audits identify potential risks and provide opportunities for enhancing security protocols.
Compliance with Regulations: Staying abreast of industry regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or specific industry standards, ensures that invoice management practices align with legal requirements.
Supplier Data Handling: Ensuring that suppliers also follow secure data handling practices when sharing invoice information is essential for end-to-end security.
Employee Training: Educating employees about data security best practices, including recognizing phishing attempts and adhering to secure procedures, strengthens the human element of data protection.
Data Retention and Destruction: Implementing clear data retention and destruction policies ensures that invoice data is stored only for the necessary period and is securely disposed of when no longer needed.
By weaving together these measures, organizations can create a robust framework that not only safeguards sensitive financial information but also demonstrates a commitment to compliance and ethical data handling. In a landscape where data breaches and regulatory infringements pose significant risks, ensuring data security and compliance within invoice management is not only a legal obligation but also a strategic imperative for maintaining organizational reputation and operational integrity.
Future Trends in Purchase Invoices and Procurement
As the tides of innovation continue to reshape industries, the realm of purchase invoices and procurement stands on the cusp of transformation. From the integration of cutting-edge technologies to the evolution of supplier relationships, the future holds a myriad of exciting possibilities that promise to elevate efficiency, transparency, and strategic decision-making.
This section explores the imminent trends that are poised to redefine the landscape of purchase invoices and procurement. By delving into the fusion of artificial intelligence, sustainability initiatives, blockchain integration, and more, this section unveils the dynamic path that organizations must navigate to stay at the forefront of modern procurement practices.
As technology advances and business priorities shift, understanding these future trends becomes instrumental in not only adapting to change but harnessing it for sustained success and innovation within the intricate world of procurement.
A. Continued evolution of e-invoicing and automation
In the trajectory of purchase invoices and procurement, the journey towards seamless efficiency and enhanced connectivity continues to be guided by the evolution of e-invoicing and automation. These twin pillars of innovation have already transformed the landscape, and their ongoing development promises to reshape processes, relationships, and decision-making even further.
The continued evolution of e-invoicing and automation encompasses:
Advanced E-Invoicing Solutions: E-invoicing is set to become more than just a digital exchange of invoices. Enhanced solutions will focus on interoperability, enabling invoices to flow seamlessly across different systems and platforms, regardless of technological disparities.
Real-Time Transactions: The future holds the promise of real-time transaction processing. E-invoicing systems will enable instant invoice generation, transmission, and verification, accelerating payment cycles and reducing delays.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning: E-invoicing will be further integrated with artificial intelligence and machine learning. Smart algorithms can enhance data extraction accuracy, identify patterns in spending, and even predict potential discrepancies.
Holistic Process Automation: Automation will transcend single processes and extend to holistic procurement workflows. End-to-end automation will seamlessly integrate purchase orders, goods receipt, and invoicing, offering a unified, streamlined ecosystem.
Cognitive Automation: Cognitive automation combines machine learning and natural language processing to enable systems to understand and interpret unstructured data from invoices. This advancement enhances accuracy and reduces the need for manual intervention.
Supplier Collaboration Platforms: Automation will extend to collaborative platforms that facilitate supplier interactions. These platforms will enable suppliers to directly input invoice data, reducing errors and expediting processes.
Digital Identities and Trust: Blockchain and digital identities will play a pivotal role in ensuring the authenticity of e-invoices, mitigating the risk of fraud and enhancing trust among stakeholders.
As e-invoicing and automation evolve, they will continue to shape the landscape of procurement, making transactions faster, more accurate, and increasingly transparent. The interconnectedness fostered by these technologies will enable organizations to cultivate stronger relationships with suppliers, make informed decisions based on real-time insights, and maintain a competitive edge in an ever-changing business landscape.
B. Integration of blockchain for secure and transparent invoice tracking
In the onward march of innovation, the integration of blockchain technology emerges as a groundbreaking force poised to revolutionize invoice tracking within procurement. Blockchain's intrinsic attributes of transparency, immutability, and decentralized consensus hold the potential to transform how purchase invoices are managed, tracked, and verified, paving the way for enhanced accountability and trust in procurement processes.
The integration of blockchain for secure and transparent invoice tracking encompasses:
Immutable Ledger: Blockchain's decentralized ledger ensures that once an invoice is recorded, it cannot be altered, providing an unchangeable record of transactions. This tamper-resistant nature enhances the reliability of invoice data.
End-to-End Transparency: Blockchain enables participants to access a shared, transparent record of all invoice-related interactions. This visibility mitigates disputes and reduces the need for manual reconciliation.
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts within blockchain technology can automate invoice-related processes. Payment terms, approvals, and delivery verification can be self-executed based on predefined conditions, streamlining workflows.
Enhanced Trust: The distributed nature of blockchain fosters trust among participants. Suppliers and buyers alike can rely on a single source of truth, reducing the need for intermediaries and building stronger partnerships.
Fraud Prevention: Blockchain's security mechanisms prevent unauthorized alterations, making it significantly more challenging for fraudulent activities such as invoice tampering or double spending to occur.
Efficient Auditing and Compliance: Auditing becomes more efficient with blockchain, as the entire history of an invoice is available in a single, verified ledger. This simplifies compliance with regulatory requirements.
Real-Time Tracking: The real-time nature of blockchain enables instant updates and notifications across the network, ensuring stakeholders are informed of changes and milestones in the invoice lifecycle.
The integration of blockchain technology within invoice tracking promises a future where data integrity, security, and trust are the bedrock of procurement processes. As organizations strive for heightened accountability and transparency, blockchain's transformative power has the potential to reshape not only how invoices are managed but also how business relationships are fostered in a rapidly evolving digital era.
C. Embracing AI and machine learning for advanced spend analytics
In the era of data-driven decision-making, the fusion of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) holds immense promise for revolutionizing the way organizations analyze and optimize their spending patterns. This synergy is set to reshape spend analytics within procurement, offering a new dimension of insights that empower organizations to make informed decisions, identify cost-saving opportunities, and enhance overall procurement efficiency.
Embracing AI and machine learning for advanced spend analytics encompasses:
Predictive Analytics: AI and ML algorithms can analyze historical spending data to predict future trends. This enables organizations to anticipate demand, optimize inventory levels, and negotiate favorable terms with suppliers.
Anomaly Detection: Machine learning algorithms can identify anomalies or outliers in spending data, flagging potential errors, fraud, or inefficiencies that might have gone unnoticed through traditional methods.
Vendor Performance Evaluation: AI-powered analytics can evaluate supplier performance across various parameters, such as delivery times, pricing consistency, and quality of goods or services. This data-driven evaluation informs supplier relationship management and negotiation strategies.
Category and Item Insights: Advanced analytics can categorize spending into granular categories, offering insights into where funds are allocated. This information guides decisions related to bulk purchasing, strategic sourcing, and resource allocation.
Real-time Insights: AI-driven analytics provide real-time insights into spending patterns. This allows organizations to react swiftly to market shifts, optimize purchasing decisions, and align procurement strategies with business goals.
Pattern Recognition: Machine learning algorithms identify patterns within spending data that may not be apparent to human analysis. These patterns can reveal opportunities for consolidation, process improvements, or cost reduction.
Customized Recommendations: AI-powered systems can generate customized recommendations based on spending history and market trends. These recommendations guide procurement professionals in making strategic decisions.
As organizations embrace AI and machine learning for advanced spend analytics, they embark on a journey that transcends traditional data analysis. By uncovering hidden insights, predicting future trends, and enabling proactive decision-making, these technologies elevate procurement from a reactive function to a strategic pillar that contributes to overall business growth and efficiency.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of business operations, the role of purchase invoices in procurement has transcended the realm of administrative paperwork. These seemingly routine documents have transformed into strategic assets that drive efficiency, transparency, and data-driven decision-making.
As we conclude our exploration of the strategic role of purchase invoices in streamlining procurement, it is evident that this journey is marked by dynamic shifts, innovative technologies, and an unwavering commitment to operational excellence.
From the early stages of identifying procurement needs to the intricacies of supplier collaboration, the procurement process is a tapestry woven with complexity. In this journey, purchase invoices serve as essential threads, connecting stakeholders, validating transactions, and illuminating strategic insights.
The integration of technology, ranging from electronic invoicing systems to AI-driven analytics, has emerged as a driving force, propelling organizations toward a future of streamlined processes and unparalleled efficiency.
Moreover, the strategic dimensions of purchase invoices are boundless. They interlace with compliance and risk management, ensuring adherence to contractual terms and guarding against discrepancies. They foster enhanced collaboration with suppliers, nurturing relationships that transcend transactional exchanges. As organizations rise to meet challenges such as complex invoice formats and data security concerns, they innovate resilient strategies that pave the way for accountability, trust, and resilience.
Looking ahead, the future beckons with exciting possibilities. Continued evolution of e-invoicing and automation promises heightened efficiency, while blockchain integration revolutionizes transparency and security. Embracing AI and machine learning for advanced spend analytics unlocks insights that fuel strategic procurement decisions.
These trends underscore the transformative journey of purchase invoices, from their humble beginnings as transaction records to their role as beacons of innovation in the procurement landscape.
As organizations navigate this transformative landscape, they recognize that purchase invoices are more than mere documents; they are conduits of progress. In their strategic integration, automated workflows, data analytics, and collaborative potential, purchase invoices shape the future of procurement as a strategic pillar that drives operational excellence, enhances supplier relationships, and propels organizations toward sustainable growth.
How Can Deskera Help You?
Deskera ERP and MRP systems help you to keep your business units organized. The system's primary functions are as follows:
- Keep track of your raw materials and final items inventories
- Control production schedules and routings
- Keep a bill of materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your own dashboards
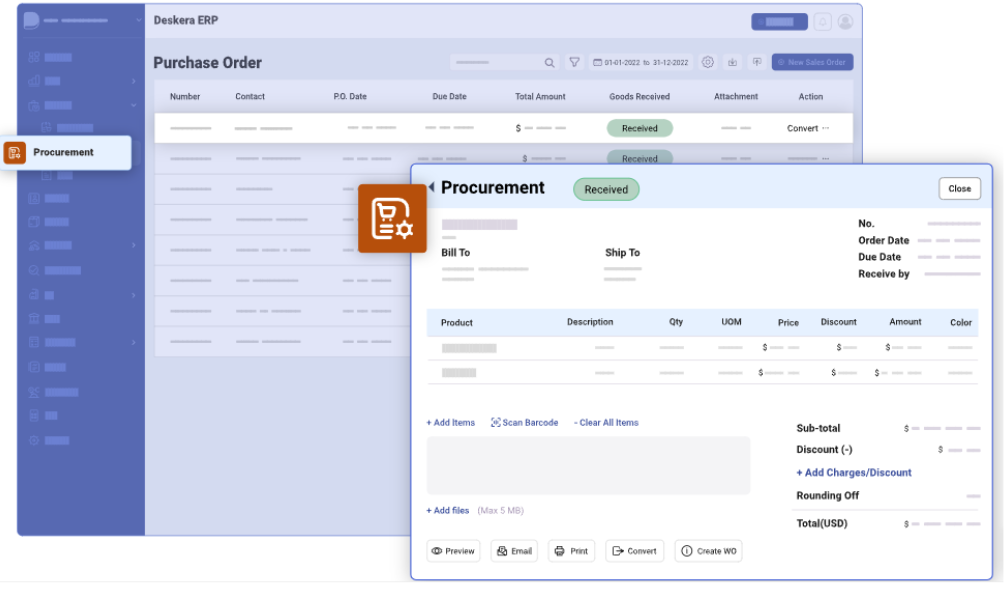
Here are some ways Deskera ERP's Procurement functionality can assist you:
- Create Requisitions and RFQs
- Generate Vendor Quotations
- Set up Vendor Scorecards
- Manage Preferred Suppliers
- Scan Purchase Invoices
- Create Purchase Orders
Deskera Books enables you to manage your accounts and finances more effectively. Maintain sound accounting practices by automating accounting operations such as billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a strong solution that manages your sales and assists you in closing agreements quickly. It not only allows you to do critical duties such as lead generation via email, but it also provides you with a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a simple tool for taking control of your human resource management functions. The technology not only speeds up payroll processing but also allows you to manage all other activities such as overtime, benefits, bonuses, training programs, and much more.
Key Takeaways
- Invoices as Strategic Assets: Purchase invoices are not mere paperwork; they are strategic assets that shape procurement practices, supplier relationships, and decision-making.
- Technology's Vanguard: Technology, including electronic invoicing systems and automation, redefines invoice management by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and transparency.
- Efficiency Through Automation: Automation expedites workflows, minimizes errors, and streamlines processes, liberating resources for value-added tasks.
- Data-Driven Insights: Invoice data analysis yields insights that drive strategic decisions, optimize spending, and enhance supplier relationships.
- Collaboration Catalyst: Purchase invoices foster collaboration with suppliers by promoting transparent communication, insights sharing, and mutual growth.
- Security and Compliance Guardians: Organizations must prioritize data security, encryption, and regulatory compliance to safeguard sensitive financial information.
- Blockchain's Transformative Potential: Integration of blockchain technology offers tamper-resistant invoice tracking, end-to-end transparency, and trust among stakeholders.
- AI and ML's Strategic Role: AI and machine learning empower advanced spend analytics, predicting trends, detecting anomalies, and guiding informed procurement decisions.
- Navigating Challenges: Strategies for handling complex invoice formats, exceptions, and discrepancies fortify processes, ensuring accuracy and resilience.
- Embracing the Future: The future of procurement unfolds through continued e-invoicing evolution, blockchain integration, AI-driven analytics, and a commitment to innovation.
These takeaways collectively underscore the metamorphosis of purchase invoices from routine transactions to pivotal agents of change within procurement. By embracing innovation, harnessing technology, and fostering collaboration, organizations can navigate the complexities of modern procurement with strategic prowess, operational excellence, and a vision for the future.
Related Articles











