Food manufacturing plays a critical role in feeding the world's population, and its importance has only grown with the increase in global demand for food products.
However, the industry is facing numerous challenges that impact its ability to produce food efficiently and sustainably. As a result, food manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to improve their efficiency and competitiveness in the market.
In this context, efficiency becomes a crucial factor for success, as it enables food manufacturers to reduce costs, improve product quality, and meet environmental standards while increasing production capacity.
Fortunately, there are numerous strategies that food manufacturers can implement to improve their efficiency. From lean manufacturing to automation and robotics, supply chain optimization, and continuous improvement, there are many proven approaches that have yielded significant benefits for food manufacturers.
These strategies not only help food manufacturers increase productivity and reduce waste, but also enable them to remain competitive and sustainable in the long run.

In this article, we will explore in detail the various strategies that food manufacturers can adopt to improve their efficiency, along with case studies and examples of successful implementation. By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the importance of efficiency in food manufacturing and how to implement these strategies effectively.
- Overview of Food Manufacturing Industry
- Importance of Efficiency in Food Manufacturing
- Current Challenges in Food Manufacturing
- Strategies for Improving Efficiency
- Automation and Robotics
- Supply Chain Optimization
- Workflow Efficiency Improvement
- How can MRP and ERP systems Assist in Improving Efficiency of Food Manufacturing?
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Overview of Food Manufacturing Industry
The food manufacturing industry is a crucial component of the global food supply chain, responsible for processing raw agricultural products into a wide variety of food and beverage products. The industry plays a vital role in meeting the demands of a growing global population, with the United Nations projecting that the world population will reach 9.7 billion by 2050.
The food manufacturing industry is diverse, encompassing various sub-sectors such as dairy, meat processing, bakery and confectionery, beverages, and packaged foods. It involves a range of activities, including processing, packaging, labeling, and distribution of food products. The industry also includes research and development of new food products, quality control, and regulatory compliance.
The food manufacturing industry faces numerous challenges, including cost pressures, fluctuating commodity prices, changing consumer preferences, and environmental concerns. The industry is also subject to a range of regulations and standards that vary by region and country, making compliance a complex process.
Despite these challenges, the food manufacturing industry continues to grow, driven by global demand for food products. The industry is also witnessing technological advancements, such as automation and robotics, that are transforming the way food is produced and processed.
Overall, the food manufacturing industry plays a critical role in feeding the world's population and will continue to do so in the future. With increasing demand for food products and a need for sustainable and efficient production, the industry is constantly evolving and adapting to meet these challenges.
Importance of Efficiency in Food Manufacturing
Efficiency is a critical factor in the success of the food manufacturing industry. It enables food manufacturers to produce food products at lower costs, improve product quality, and meet environmental standards while increasing production capacity. Here are some of the reasons why efficiency is essential in food manufacturing:
- Cost reduction: Efficiency enables food manufacturers to reduce costs by minimizing waste, optimizing processes, and reducing downtime. This, in turn, can help manufacturers remain competitive in a global market that is increasingly cost-sensitive.
- Improved product quality: Efficient processes can help ensure consistent and high-quality products. This is important for building brand reputation and maintaining customer loyalty.
- Meeting environmental standards: Food manufacturing can have a significant environmental impact, from water and energy consumption to waste generation. Efficiency strategies such as reducing energy usage, water consumption, and waste generation can help food manufacturers meet environmental regulations and reduce their ecological footprint.
- Increased production capacity: Efficient processes can enable food manufacturers to produce more products in less time. This can be especially important during times of high demand or when expanding into new markets.
- Enhanced worker safety: Efficiency strategies such as automation and robotics can help reduce the risk of workplace injuries by removing workers from hazardous tasks.
Efficiency is critical for the success of food manufacturing, enabling manufacturers to reduce costs, improve product quality, meet environmental standards, increase production capacity, and enhance worker safety.
Current Challenges in Food Manufacturing
The food manufacturing industry is facing a range of challenges, including cost pressures, quality control, changing consumer preferences, environmental concerns, labor shortages, and supply chain disruptions, which are impacting its ability to produce food efficiently and sustainably. Addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions and a commitment to sustainability and continuous improvement.
High Demand and Competition
High demand and competition are significant challenges faced by the food manufacturing industry. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food products is increasing, and food manufacturers are under pressure to meet this demand while maintaining the quality and safety of their products. Here are some of the ways high demand and competition are challenging the food manufacturing industry:
- Pressure to increase production: Food manufacturers must produce more products in less time to keep up with demand. This can be challenging, especially during peak seasons or when introducing new products.
- Risk of supply chain disruptions: High demand can strain the supply chain, leading to shortages of raw materials or finished products. This can impact production and result in lost sales and customer dissatisfaction.
- Need for innovation: Consumers are increasingly demanding new and innovative food products, which can be challenging for food manufacturers to develop and introduce to the market quickly.
- Cost pressures: Increasing demand can lead to higher costs for raw materials, labor, and energy. Food manufacturers must balance the need to keep costs low while meeting demand and maintaining product quality.
- Competition from global markets: The food manufacturing industry is global, and manufacturers face competition from other countries that can produce products at lower costs. This can impact the profitability of domestic food manufacturers and result in the loss of market share.
High demand and competition are significant challenges for the food manufacturing industry, requiring food manufacturers to balance the need for increased production with the cost pressures of maintaining quality, innovation, and profitability. To overcome these challenges, food manufacturers must be agile, innovative, and customer-focused, with a commitment to sustainability and continuous improvement.
Cost Pressures
Cost pressures are a significant challenge facing the food manufacturing industry. Several factors contribute to these pressures, including rising commodity prices, increasing energy costs, and growing competition. Here are some ways in which cost pressures impact the food manufacturing industry:
- Lower profit margins: Food manufacturers face increasing pressure to maintain low prices to remain competitive. This can lead to lower profit margins and financial instability, making it challenging to invest in innovation, research, and development.
- Reduced investment in technology and innovation: Cost pressures can limit the ability of food manufacturers to invest in technology and innovation. This can reduce efficiency and slow down the development of new products and processes, leading to stagnation in the industry.
- Reduced quality and safety: Cost pressures can lead to reduced investment in quality control and safety measures, which can impact product quality and safety. This can result in regulatory violations, product recalls, and damage to brand reputation.
- Inability to invest in sustainability: Cost pressures can limit the ability of food manufacturers to invest in sustainability initiatives such as reducing waste, water conservation, and renewable energy. This can lead to negative environmental impacts and non-compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Inability to compete: Cost pressures can make it difficult for food manufacturers to compete with larger companies that have economies of scale and can produce products at lower costs. This can lead to loss of market share and ultimately business failure.
Quality Control
Quality control is a significant challenge in the food manufacturing industry, and it involves ensuring that food products meet the required quality and safety standards. Here are some ways in which quality control is a challenge for food manufacturers:
- Food safety regulations: Food manufacturers must comply with strict food safety regulations and standards set by various regulatory bodies such as the FDA, USDA, and EPA. Failure to comply can result in fines, product recalls, and damage to brand reputation.
- Consistency in product quality: Food manufacturers must ensure that their products have consistent quality in terms of taste, texture, appearance, and nutritional content. Achieving consistency can be challenging, especially when using natural ingredients and dealing with seasonal variations.
- Testing for contaminants: Food manufacturers must test their products for contaminants such as pathogens, allergens, and chemical residues. This testing can be time-consuming and expensive, and failure to detect contaminants can lead to health risks for consumers.
- Traceability and labeling: Food manufacturers must track their products from raw materials to finished products to ensure traceability and accurate labeling. This can be challenging, especially when dealing with complex supply chains and multiple ingredients.
- Consumer demands: Consumers are increasingly demanding high-quality, natural, and organic food products. Meeting these demands can be challenging, especially for food manufacturers that use artificial ingredients, preservatives, or pesticides.
Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations are a significant challenge in the food manufacturing industry, and they involve complying with laws and regulations that aim to protect the environment. Here are some ways in which environmental regulations are a challenge for food manufacturers:
- Compliance costs: Compliance with environmental regulations can be costly, especially for small and medium-sized food manufacturers. The costs can include expenses related to waste disposal, energy efficiency, and pollution control.
- Impact on production: Environmental regulations can impact production processes by limiting the use of certain materials or requiring the adoption of new technologies. This can increase production costs and reduce efficiency.
- Supply chain complexity: Environmental regulations can affect the entire supply chain, from raw material sourcing to product distribution. Food manufacturers must ensure that their suppliers and distributors comply with environmental regulations, which can add complexity to the supply chain.
- Brand reputation: Environmental regulations violations can damage a food manufacturer's brand reputation, leading to reduced customer loyalty and decreased sales.
- Innovation and competitiveness: Environmental regulations can drive innovation in the food manufacturing industry by requiring the development of new, sustainable technologies and practices. However, complying with regulations can also make it difficult for food manufacturers to compete with companies that are not subject to the same regulations.
Labor Shortage
Labor shortage is a significant challenge in the food manufacturing industry, and it involves a lack of skilled and available workers to meet the demand for labor. Here are some ways in which labor shortage is a challenge for food manufacturers:
- Recruitment difficulties: Food manufacturers may struggle to find qualified and skilled workers to fill open positions. This can lead to extended recruitment periods, higher recruitment costs, and increased turnover rates.
- Training and skill development: Food manufacturers may need to invest in training and skill development programs to attract and retain workers. This can be costly and time-consuming, especially when dealing with a transient workforce.
- Production delays: Labor shortages can lead to production delays and disruptions, affecting a company's ability to meet customer demand and maintain supply chain stability.
- Safety concerns: Labor shortages can lead to overworked and fatigued employees, which can increase the risk of workplace accidents and injuries.
- Automation challenges: Labor shortages can make it challenging for food manufacturers to invest in automation and other labor-saving technologies, which may require significant capital investments.
Strategies for Improving Efficiency
Implementing effective strategies to improve the efficiency of food manufacturing operations is crucial for companies to remain competitive in the current market, address challenges such as high demand, cost pressures, quality control, environmental regulations, and labor shortage, and achieve sustainable growth and profitability in the long run.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is a strategy for improving the efficiency of food manufacturing operations by reducing waste, increasing productivity, and improving quality. The goal of lean manufacturing is to eliminate activities and processes that do not add value to the final product, while optimizing those that do. Here are some ways in which lean manufacturing can be implemented in food manufacturing:
- Value stream mapping: Value stream mapping is a lean tool used to identify inefficiencies and waste in the production process. This helps food manufacturers to identify areas where improvements can be made to streamline the process and reduce costs.
- Continuous improvement: Continuous improvement is a core principle of lean manufacturing. It involves ongoing efforts to improve processes and reduce waste, which can lead to increased productivity and efficiency.
- Just-in-time (JIT) production: JIT production is a lean manufacturing technique that involves producing products only when they are needed, in the quantities required. This reduces inventory levels and storage costs while ensuring that customers receive their orders on time.
- Standardization: Standardization is a key aspect of lean manufacturing, as it helps to reduce variation in processes and ensure that they are performed consistently. This can help to improve quality and reduce the risk of errors and defects.
- Employee involvement: Lean manufacturing encourages employee involvement in process improvement efforts, as they are often the ones who are most familiar with the production process. This can lead to increased employee engagement and satisfaction, as well as better process outcomes.
By implementing lean techniques such as value stream mapping, continuous improvement, JIT production, standardization, and employee involvement, food manufacturers can optimize their production processes and achieve sustainable growth and profitability.
Examples of Lean Tools and Techniques in Food Manufacturing
Lean tools and techniques are crucial for improving the efficiency of food manufacturing operations. Here are some examples of lean tools and techniques that can be used in food manufacturing:
- 5S: 5S is a lean tool used to organize the workplace and reduce waste. The 5S approach involves sorting, setting in order, shining, standardizing, and sustaining. In food manufacturing, 5S can be used to organize the production area, reduce clutter, and ensure that tools and materials are easily accessible.
- Kanban: Kanban is a visual scheduling tool used to manage inventory levels and production processes. In food manufacturing, Kanban can be used to ensure that raw materials and ingredients are available when needed, and that production processes are synchronized to meet customer demand.
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM): TPM is a lean tool used to optimize equipment performance and minimize downtime. In food manufacturing, TPM can be used to ensure that production equipment is maintained properly, and that operators are trained to perform routine maintenance tasks.
- Kaizen: Kaizen is a continuous improvement approach used to identify and eliminate waste in production processes. In food manufacturing, Kaizen can be used to identify process inefficiencies and implement solutions to improve efficiency, quality, and safety.
- Standardized Work: Standardized work involves creating a clear and documented process for performing tasks, which can help to reduce variation and ensure consistent results. In food manufacturing, standardized work can be used to ensure that employees perform tasks consistently and to improve quality.
- Andon: Andon is a visual alert system used to signal problems or issues on the production line. In food manufacturing, Andon can be used to alert operators and supervisors to production issues, allowing them to address problems quickly and efficiently.
Overall, lean tools and techniques can help food manufacturers to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and optimize production processes.
Benefits of Implementing Lean Manufacturing
Implementing lean manufacturing in food manufacturing operations can provide numerous benefits. Here are some of the key benefits of implementing lean manufacturing in food manufacturing:
- Reduced waste: Lean manufacturing focuses on identifying and reducing waste in the production process. By eliminating unnecessary steps, reducing inventory levels, and optimizing production processes, food manufacturers can reduce waste and improve efficiency.
- Increased productivity: Lean manufacturing techniques such as standardized work, continuous improvement, and just-in-time (JIT) production can increase productivity by ensuring that production processes are optimized and that resources are used efficiently.
- Improved quality: Lean manufacturing can help to improve product quality by identifying and eliminating sources of variation in the production process. By standardizing processes, using visual controls, and implementing quality checks, food manufacturers can ensure that products meet customer requirements and regulatory standards.
- Lower costs: Lean manufacturing can help to reduce costs by eliminating waste, reducing inventory levels, and optimizing production processes. This can lead to lower operating costs, lower material costs, and higher profits.
- Increased flexibility: Lean manufacturing can help food manufacturers to be more flexible and responsive to changes in customer demand. By implementing JIT production, using visual controls, and encouraging employee involvement, food manufacturers can adjust production processes quickly and efficiently to meet changing customer needs.
- Improved employee engagement: Lean manufacturing techniques such as employee involvement, continuous improvement, and standardized work can improve employee engagement by giving employees a sense of ownership and accountability for their work. This can lead to increased job satisfaction, better performance, and lower turnover rates.
By adopting a lean mindset and implementing lean tools and techniques, food manufacturers can achieve sustainable growth and profitability, while meeting customer demand and ensuring product quality and safety.
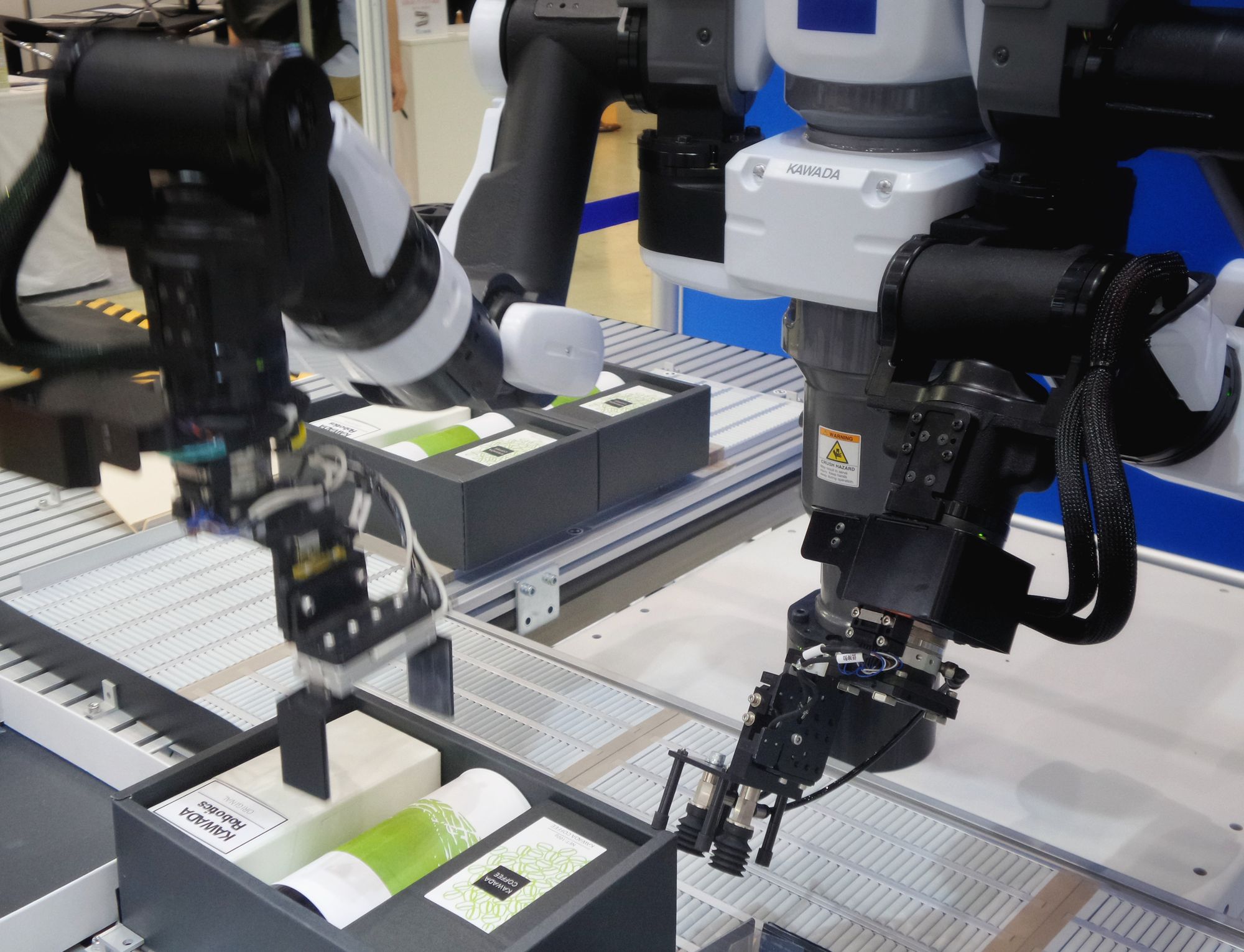
Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are emerging as important strategies for improving the efficiency of food manufacturing. Automation involves the use of technology to automate production processes, while robotics involves the use of robots to perform tasks traditionally done by humans.
In food manufacturing, automation and robotics can be used to perform repetitive, labor-intensive tasks such as packaging, labeling, and sorting. By automating these tasks, food manufacturers can improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and increase productivity.
Here are some specific examples of how automation and robotics are being used in food manufacturing:
- Packaging: Automated packaging systems can be used to fill and seal containers, reducing the need for manual labor. This can improve efficiency and reduce labor costs, while ensuring that products are packaged consistently and to regulatory standards.
- Labeling: Automated labeling systems can be used to apply labels to products, reducing the need for manual labor. This can improve efficiency and reduce the risk of errors in labeling.
- Sorting: Automated sorting systems can be used to sort products by size, shape, color, or other characteristics. This can improve efficiency and reduce labor costs, while ensuring that products are sorted accurately and to customer specifications.
- Processing: Robotics can be used to perform tasks such as cutting, slicing, and dicing, which are traditionally done by humans. This can improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and increase productivity, while ensuring that products are processed consistently and to regulatory standards.
- Quality control: Automated systems can be used to inspect products for quality and safety, reducing the need for manual labor. This can improve efficiency and ensure that products meet regulatory standards.
Overall, automation and robotics can help food manufacturers to improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and increase productivity, while ensuring that products are produced consistently and to regulatory standards. By implementing these technologies, food manufacturers can achieve sustainable growth and profitability, while meeting customer demand and ensuring product quality and safety.
Types of Automation and Robotics Used in Food Manufacturing
There are various types of automation and robotics used in food manufacturing to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs. Here are some examples:
- Robotic arms: These are used to perform tasks such as cutting, slicing, and dicing. Robotic arms can be programmed to perform tasks precisely and consistently, reducing the need for manual labor.
- Automated packaging systems: These are used to fill and seal containers, reducing the need for manual labor. Automated packaging systems can be programmed to package products consistently and to regulatory standards.
- Automated labeling systems: These are used to apply labels to products, reducing the need for manual labor. Automated labeling systems can be programmed to apply labels accurately and consistently.
- Automated sorting systems: These are used to sort products by size, shape, color, or other characteristics. Automated sorting systems can be programmed to sort products accurately and efficiently.
- Automated inspection systems: These are used to inspect products for quality and safety, reducing the need for manual labor. Automated inspection systems can be programmed to inspect products consistently and to regulatory standards.
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs): These are used to transport materials and products within a manufacturing facility. AGVs can be programmed to navigate within a facility and transport materials and products efficiently.
- Collaborative robots (cobots): These are robots designed to work alongside humans in a manufacturing facility. Cobots can be programmed to perform tasks that are difficult or unsafe for humans to perform, reducing the risk of injury and improving efficiency.
By implementing these technologies, food manufacturers can achieve sustainable growth and profitability, while meeting customer demand and ensuring product quality and safety.
Benefits and Challenges of Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics offer several benefits to food manufacturers, including improved efficiency, increased productivity, and reduced labor costs. However, there are also some challenges associated with implementing these technologies. Here are some of the benefits and challenges of automation and robotics in food manufacturing:
Benefits:
- Improved efficiency: Automation and robotics can perform tasks faster and more consistently than humans, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
- Increased productivity: Automation and robotics can work around the clock, leading to increased productivity and throughput.
- Reduced labor costs: Automation and robotics can reduce the need for manual labor, leading to reduced labor costs.
- Improved quality control: Automation and robotics can perform tasks consistently and accurately, leading to improved quality control.
- Increased safety: Automation and robotics can perform tasks that are difficult or dangerous for humans to perform, leading to increased safety in the manufacturing facility.
Challenges:
- High upfront costs: Implementing automation and robotics can be expensive, with high upfront costs for equipment, software, and training.
- Complex integration: Integrating automation and robotics into existing manufacturing processes can be complex and time-consuming.
- Maintenance and repair: Automation and robotics require regular maintenance and repair, which can be costly and time-consuming.
- Dependence on technology: A reliance on automation and robotics can leave manufacturers vulnerable to technological failures or disruptions.
- Resistance to change: Some employees may resist the introduction of automation and robotics, leading to cultural challenges in the manufacturing facility.
While automation and robotics offer several benefits to food manufacturers, there are also challenges that must be addressed in order to successfully implement these technologies. By carefully considering the benefits and challenges, food manufacturers can determine if automation and robotics are the right choice for their business, and develop a strategy for successful implementation.
Examples of Successful Implementation
Here are some examples of successful implementation of automation and robotics in food manufacturing:
- Nestlé: Nestlé has implemented automation and robotics in their coffee manufacturing facility in Japan. The facility uses robots to package coffee capsules and can produce up to 900,000 capsules per day with minimal human intervention.
- PepsiCo: PepsiCo has implemented robotics in their snack manufacturing facility in the United States. The facility uses robots to palletize and package products, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing efficiency.
- Kraft Heinz: Kraft Heinz has implemented automation and robotics in their cheese manufacturing facility in the United States. The facility uses robots to cut and package cheese, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing efficiency.
- Danone: Danone has implemented automation and robotics in their yogurt manufacturing facility in France. The facility uses robots to fill and package yogurt cups, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing efficiency.
- Tyson Foods: Tyson Foods has implemented robotics in their poultry processing facility in the United States. The facility uses robots to debone and portion chicken, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing efficiency.
In all these examples, the implementation of automation and robotics has led to improved efficiency, increased productivity, and reduced labor costs. By implementing these technologies, food manufacturers can achieve sustainable growth and profitability, while meeting customer demand and ensuring product quality and safety.
Supply Chain Optimization
Supply chain optimization is a strategy for improving the efficiency of food manufacturing by streamlining the entire supply chain from raw materials to finished products. It involves analyzing and optimizing every aspect of the supply chain, including inventory management, transportation, warehousing, and distribution.
One key aspect of supply chain optimization in food manufacturing is reducing waste and improving inventory management. By accurately forecasting demand and managing inventory levels, food manufacturers can reduce waste and save costs. This can be achieved through the use of technology, such as advanced analytics and inventory management software, to track inventory levels and predict demand.
Another aspect of supply chain optimization is improving transportation and distribution. This involves optimizing logistics and transportation routes to minimize transportation costs and reduce lead times. It also involves improving the accuracy and efficiency of order processing and fulfillment, to ensure that products are delivered to customers on time and in good condition.
In addition to improving efficiency, supply chain optimization can also improve the sustainability of food manufacturing. By reducing waste and optimizing transportation, food manufacturers can reduce their carbon footprint and minimize their impact on the environment.
Overall, supply chain optimization is an important strategy for improving the efficiency of food manufacturing. By streamlining the entire supply chain and reducing waste, food manufacturers can achieve sustainable growth and profitability while meeting customer demand and ensuring product quality and safety.
Importance of a Well-Managed Supply Chain
A well-managed supply chain is critical for the success of food manufacturing sector for several reasons:
- Cost efficiency: A well-managed supply chain helps to minimize costs associated with transportation, storage, and inventory. By optimizing the supply chain, food manufacturers can reduce waste and avoid overproduction, which can result in significant cost savings.
- Improved quality control: A well-managed supply chain ensures that raw materials and finished products are tracked and monitored throughout the entire manufacturing process. This helps to identify and address quality issues quickly, ensuring that only high-quality products reach consumers.
- Meeting customer demands: With a well-managed supply chain, food manufacturers can quickly respond to changes in customer demand and adjust their production accordingly. This helps to ensure that products are always available when and where they are needed, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Compliance with regulations: In the food manufacturing sector, there are numerous regulations and safety standards that must be met. A well-managed supply chain helps to ensure compliance with these regulations, reducing the risk of costly fines and legal issues.
- Sustainability: A well-managed supply chain can help to reduce waste and minimize the environmental impact of food manufacturing operations. This can include reducing energy consumption, optimizing transportation routes, and minimizing packaging waste.
By optimizing the supply chain, food manufacturers can improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance quality control, and meet customer demands, all while ensuring compliance with regulations and promoting sustainability.
Key Strategies for Optimizing the Food Supply Chain
There are several key strategies for optimizing the food supply chain:
- Use data analytics: Advanced analytics tools can help food manufacturers to better understand customer demand, optimize inventory levels, and improve transportation efficiency. By leveraging data insights, food manufacturers can make more informed decisions about production and distribution.
- Collaborate with suppliers and distributors: Collaborating with suppliers and distributors can help to streamline the supply chain and improve communication. By working together, food manufacturers can optimize transportation routes, reduce lead times, and minimize waste.
- Adopt new technologies: The use of new technologies, such as blockchain and internet of things (IoT) devices, can help to improve supply chain transparency and traceability. This can help to reduce the risk of food safety incidents and improve quality control.
- Implement a lean manufacturing approach: Lean manufacturing principles, such as just-in-time production and waste reduction, can help to improve efficiency and reduce costs. By eliminating waste and optimizing production processes, food manufacturers can improve profitability and sustainability.
- Focus on sustainability: Sustainability is becoming increasingly important to consumers and regulators. By focusing on sustainability throughout the supply chain, food manufacturers can reduce waste, minimize their environmental impact, and meet the evolving demands of consumers.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): WMS software can be used to optimize inventory levels and improve warehouse efficiency. By automating processes such as picking and packing, WMS can help to reduce errors and improve productivity.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze data from the supply chain and identify patterns and trends. This can help to improve demand forecasting, optimize inventory levels, and reduce waste.
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI): EDI technology can be used to automate the exchange of information between different parties within the supply chain. This can help to improve communication and reduce the risk of errors.
- Transportation Management Systems (TMS): TMS software can be used to optimize transportation routes and improve delivery times. By integrating with GPS tracking and other technologies, TMS can provide real-time visibility into transportation operations.
Workflow Efficiency Improvement
Workflow efficiency improvement involves the streamlining of processes and procedures within a food manufacturing facility to improve productivity, reduce waste, and enhance quality control. By optimizing workflows, manufacturers can achieve greater consistency in their operations, minimize errors and delays, and ultimately improve their bottom line.
Some key strategies for improving workflow efficiency in food manufacturing include:
- Standardization: By standardizing procedures and processes, manufacturers can ensure that every step in the production process is performed in a consistent manner. This can help to reduce errors and delays, and improve overall productivity.
- Automation: By automating certain tasks, such as data entry, inventory tracking, and quality control, manufacturers can reduce the risk of errors and improve productivity. Automation can also free up staff time for more value-added tasks.
- Lean principles: By adopting lean principles, such as value stream mapping and continuous improvement, manufacturers can identify and eliminate waste in their operations. This can lead to significant improvements in efficiency and productivity.
- Employee training: By providing employees with the necessary training and resources, manufacturers can improve the skills and knowledge of their workforce, leading to better quality control, greater efficiency, and higher job satisfaction.
- Data analysis: By collecting and analyzing data on production processes and outcomes, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement and optimize workflows accordingly.
Improving workflow efficiency can help food manufacturers to meet customer demands, reduce waste and costs, and enhance quality control, all of which are crucial for success in a highly competitive and challenging industry.
Examples of Workflow Efficiency Improvement initiatives in Food Manufacturing
Here are some examples of workflow efficiency improvement initiatives that have been implemented in the food manufacturing industry:
- Batch processing: Implementing batch processing to streamline production processes and reduce the amount of downtime between runs.
- Lean manufacturing: Adopting lean manufacturing principles to eliminate waste, reduce costs, and improve quality control.
- Standardized work procedures: Standardizing work procedures to ensure consistency and reduce the risk of errors.
- Automated systems: Implementing automated systems for tasks such as inventory management, quality control, and production scheduling.
- Cross-training employees: Cross-training employees to increase their skill sets and flexibility, allowing them to perform a wider range of tasks and reducing the need for specialized workers.
- Real-time data monitoring: Implementing real-time data monitoring and analysis to identify and address production issues quickly, reducing downtime and waste.
- Preventive maintenance: Implementing a preventive maintenance program to keep equipment in good working condition and reduce the risk of breakdowns and downtime.
By implementing these initiatives, food manufacturers can improve their workflow efficiency, reduce costs, increase productivity, and enhance quality control, leading to improved profitability and competitiveness in the industry.
Benefits of a Workflow Efficiency Improvement Culture
Developing a culture of workflow efficiency improvement in food manufacturing can provide numerous benefits, including:
- Increased productivity: Improving workflow efficiency can lead to higher productivity levels by reducing the amount of time and resources required to complete tasks.
- Reduced costs: By eliminating waste and reducing downtime, a culture of workflow efficiency improvement can lead to significant cost savings.
- Improved quality: Streamlining processes and implementing quality control measures can improve the overall quality of products, reducing the risk of defects and recalls.
- Increased employee satisfaction: Employees who are engaged in the improvement process and have the tools and resources to work efficiently are more likely to be satisfied with their jobs and feel empowered to contribute to the success of the organization.
- Enhanced competitiveness: Food manufacturers that prioritize workflow efficiency and continuously look for ways to improve their operations are better positioned to compete in the marketplace, both in terms of cost and quality.
- Greater flexibility: By improving workflow efficiency and increasing employee skills, organizations can become more flexible in responding to changes in market demand and production needs.
Comparison of Different Approaches and their Results
There are several approaches that food manufacturers can take to improve the efficiency of their operations, including lean manufacturing, automation and robotics, supply chain optimization, and workflow efficiency improvement. While each approach has its own benefits and challenges, comparing them can help manufacturers determine which approach may be most appropriate for their specific needs.
Lean manufacturing, for example, emphasizes the elimination of waste and the creation of standardized work procedures to improve efficiency and quality control. This approach has been shown to reduce costs and improve quality, but it requires a significant investment in training and culture change.
Automation and robotics, on the other hand, involve the use of advanced technology to automate production processes and reduce the need for human labor. This approach can lead to significant increases in efficiency, but requires a substantial upfront investment and ongoing maintenance and upgrading costs.
Supply chain optimization involves the use of technology and process improvements to improve the flow of goods and materials through the supply chain, reducing the risk of delays and errors. This approach can improve efficiency and reduce costs, but requires significant coordination and collaboration across multiple organizations.
Workflow efficiency improvement involves streamlining processes and improving employee training and communication to reduce waste and improve quality control. This approach can lead to significant increases in productivity and employee satisfaction, but requires ongoing effort to maintain and continually improve processes.
Ultimately, the choice of approach will depend on a variety of factors, including the specific needs of the organization, the available resources and expertise, and the level of investment required. By comparing the benefits and challenges of each approach, food manufacturers can make an informed decision and implement the approach that is most likely to improve their efficiency and competitiveness over the long term.
How can MRP and ERP systems Assist in Improving Efficiency of Food Manufacturing?
MRP (Material Requirements Planning) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems can assist in improving the efficiency of food manufacturing in several ways:
- Inventory management: MRP and ERP systems can help food manufacturers optimize their inventory levels by providing real-time information on inventory levels and usage rates. This can reduce inventory carrying costs and prevent overstocking or stockouts, which can result in production delays and higher costs.
- Demand forecasting: These systems can help forecast demand for raw materials and finished goods, enabling manufacturers to adjust production schedules and ensure that they have the right materials and quantities available when needed.
- Production planning: MRP and ERP systems can assist in planning production schedules, which can help to minimize downtime and maximize production efficiency. These systems can also assist in tracking production progress and identifying potential bottlenecks.
- Quality control: MRP and ERP systems can track quality data and help ensure that products meet the required standards. This can help prevent waste and reduce the risk of product recalls.
- Supply chain management: These systems can assist in managing the entire supply chain, from raw material suppliers to distribution channels, to ensure that all components are working efficiently and effectively.
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera ERP and MRP systems help you to keep your business units organized. The system's primary functions are as follows:
- Keep track of your raw materials and final items inventories
- Control production schedules and routings
- Keep a bill of materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your own dashboards
Deskera's integrated financial planning tools enable investors to better plan and track their investments. It can assist investors in making faster and more accurate decisions.
Deskera Books allows you to better manage your accounts and finances. Maintain good accounting practices by automating tasks like billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a powerful solution that manages your sales and helps you close deals quickly. It not only enables you to perform critical tasks like lead generation via email, but it also gives you a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a straightforward tool for centralizing your human resource management functions.
Key Takeaways
- The food manufacturing industry faces numerous challenges, including high demand, cost pressures, quality control, environmental regulations, and labor shortages.
- Improving efficiency is essential for food manufacturers to remain competitive and meet customer demands.
- Lean manufacturing is a popular approach that emphasizes the elimination of waste and the creation of standardized work procedures to improve efficiency and quality control.
- Automation and robotics can help manufacturers reduce the need for human labor and improve efficiency, but requires a substantial upfront investment.
- Supply chain optimization involves the use of technology and process improvements to improve the flow of goods and materials through the supply chain, reducing the risk of delays and errors.
- Workflow efficiency improvement involves streamlining processes and improving employee training and communication to reduce waste and improve quality control.
- Implementing any strategy requires a significant investment in training, culture change, and ongoing maintenance and upgrading costs.
- Collaboration and coordination across multiple organizations is essential for supply chain optimization to be successful.
- Implementation of technology solutions, such as sensors and real-time tracking, can help improve supply chain visibility and reduce the risk of disruptions.
- Workflow efficiency improvement requires ongoing effort to maintain and continually improve processes.
- Manufacturers must ensure that their implementation strategies align with their overall business goals and values.
- Improved efficiency can lead to cost savings, increased productivity, improved product quality, and higher customer satisfaction.
- The success of any strategy depends on the commitment and engagement of employees at all levels of the organization.
- Food manufacturers must prioritize sustainability and environmental responsibility in their operations.
- Continuous improvement and adaptation to changing market conditions and customer demands are essential for long-term success in the food manufacturing industry.
Related Articles