Why do maintenance schedules fail even when teams are experienced and well-staffed? Because maintenance isn’t just about knowing what needs to be fixed—it’s about knowing when and how to do it without disrupting operations. Poorly structured maintenance schedules often lead to unplanned downtime, rushed repairs, and rising maintenance costs. This is why maintenance scheduling has become a strategic priority rather than a routine administrative task.
Maintenance scheduling is the process of assigning the right maintenance tasks to the right resources at the right time. When done effectively, it ensures equipment reliability, balances technician workloads, and aligns maintenance activities with production plans. In contrast, weak scheduling practices force teams into reactive firefighting mode, increasing asset wear and shortening equipment lifecycles.
As operations grow more complex, traditional spreadsheet-based scheduling struggles to keep up. Modern maintenance teams must coordinate labor availability, spare parts, asset criticality, and production timelines—all while responding to unexpected breakdowns. Following proven best practices helps organizations move from reactive maintenance to a structured, data-driven approach that improves uptime and operational efficiency.
This is where Deskera MRP plays a critical role in enabling smarter maintenance scheduling. Deskera MRP provides centralized visibility into assets, maintenance tasks, and resource availability, helping teams plan and adjust schedules with confidence. By integrating maintenance planning with inventory and production data, it ensures spare parts availability, reduces delays, and supports proactive maintenance decisions across the shop floor.
What Is Maintenance Scheduling?
Maintenance scheduling is the process through which the maintenance department plans, organizes, and coordinates maintenance activities to keep equipment and facilities in optimal working condition. It involves deciding when maintenance tasks should be performed, who should perform them, and what resources—such as tools, spare parts, and time—are required. Rather than reacting to breakdowns, maintenance scheduling brings structure and predictability to maintenance operations.
Unscheduled equipment downtime remains one of the biggest operational challenges for organizations. According to maintenance experts, the leading causes of unplanned downtime include aging equipment (34%), mechanical failure (20%), operator error (11%), lack of time for maintenance (9%), and poor equipment design (8%) (Plant Engineering, 2020). Effective maintenance scheduling directly addresses these issues by ensuring maintenance activities are planned in advance, reducing last-minute repairs and operational disruptions.
At its core, maintenance scheduling is a strategic function within maintenance management. It covers a wide range of activities, including routine inspections, preventive maintenance, and corrective repairs. By following a well-defined schedule, organizations can identify potential issues early, prevent unexpected equipment failures, and maintain consistent asset performance. This systematic approach not only minimizes downtime but also extends equipment lifespan and improves overall operational efficiency.
The primary objective of maintenance scheduling is to balance reliability with efficiency. A structured maintenance schedule ensures that assets receive timely care without interfering with production schedules. Over time, this leads to higher productivity, lower maintenance costs, and better use of labor and resources—making maintenance scheduling a critical contributor to long-term operational success.
Maintenance Scheduling vs. Maintenance Planning
Although often used interchangeably, maintenance planning and maintenance scheduling serve distinct but complementary roles in maintenance management. Understanding the difference between the two helps organizations allocate resources more effectively, reduce downtime, and improve maintenance execution. While planning focuses on what needs to be done and how, scheduling determines when and by whom the work will be carried out.
Maintenance Planning
Maintenance planning is the strategic, preparatory phase of maintenance management. It defines the scope of work and ensures that everything required to complete a maintenance task is identified in advance. Effective planning reduces uncertainty and prevents delays during execution.
Key aspects of maintenance planning include:
- Defining maintenance tasks and job steps
- Identifying required tools, spare parts, and materials
- Estimating labor hours and skill requirements
- Creating standardized job plans and procedures
- Assessing safety requirements and compliance needs
Maintenance planning ensures that work orders are ready for execution before they reach the schedule, minimizing rework and wasted time.
Maintenance Scheduling
Maintenance scheduling is the execution-focused phase that assigns planned maintenance tasks to specific time slots and resources. It translates maintenance plans into actionable timelines that align with production schedules and workforce availability.
Key aspects of maintenance scheduling include:
- Assigning maintenance tasks to specific dates and shifts
- Allocating technicians based on skills and availability
- Coordinating maintenance windows with operations
- Managing priorities between preventive and corrective work
- Adjusting schedules to handle emergencies and breakdowns
Maintenance scheduling ensures that planned work is carried out efficiently, with minimal disruption to operations and maximum asset uptime.
In summary, maintenance planning prepares the work, while maintenance scheduling executes the plan. Together, they create a structured maintenance process that improves reliability, controls costs, and supports long-term operational efficiency.
Why Effective Maintenance Scheduling Matters
Effective maintenance scheduling goes beyond simply assigning dates to maintenance tasks—it plays a critical role in ensuring equipment reliability, operational continuity, and cost control. When maintenance activities are scheduled strategically, organizations can move from reactive firefighting to proactive asset management, improving both short-term performance and long-term sustainability.
Reduces Unplanned Downtime
A well-structured maintenance schedule ensures that inspections, servicing, and preventive tasks are performed before minor issues escalate into major failures. By addressing potential problems early, organizations can significantly reduce unexpected breakdowns that disrupt production and impact delivery timelines.
Improves Equipment Reliability and Asset Lifespan
Consistent and timely maintenance helps equipment operate within optimal conditions. Effective scheduling ensures that assets receive the care they need at the right intervals, reducing wear and tear, improving reliability, and extending the overall lifespan of machinery and facilities.
Optimizes Labor and Resource Utilization
Maintenance scheduling helps balance technician workloads and ensures that the right skills are available when needed. By aligning labor, tools, and spare parts in advance, organizations can eliminate idle time, reduce overtime, and make better use of limited maintenance resources.
Aligns Maintenance with Production and Operations
Poorly timed maintenance can disrupt production schedules and create operational bottlenecks. Effective maintenance scheduling coordinates maintenance windows with production plans, allowing essential work to be completed without interfering with critical operations or output targets.
Enhances Safety and Compliance
Regularly scheduled maintenance reduces the risk of equipment-related accidents and failures. By ensuring that inspections and safety-related tasks are completed on time, organizations can maintain compliance with regulatory standards and create a safer working environment.
Lowers Maintenance and Operational Costs
Proactive maintenance scheduling reduces emergency repairs, rush part orders, and unplanned downtime—all of which drive up costs. Over time, this structured approach helps organizations control maintenance expenses while improving overall operational efficiency.
Effective maintenance scheduling is not just a tactical activity—it is a strategic enabler that supports reliability, productivity, safety, and cost efficiency across the organization.
Common Maintenance Scheduling Challenges
Despite its importance, maintenance scheduling is often difficult to execute consistently. Operational constraints, data gaps, and coordination issues can all undermine even well-planned schedules.
Below are the most common challenges organizations face when managing maintenance schedules.
Conflicting Priorities Between Maintenance and Production
Production demands often take precedence over maintenance activities, leading to frequent schedule changes or deferred maintenance. When maintenance windows are postponed to meet output targets, equipment health suffers, increasing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and long-term reliability issues.
Unplanned Breakdowns and Emergency Work
Unexpected equipment failures disrupt planned schedules and force maintenance teams into reactive mode. Emergency work orders consume labor and resources that were allocated for preventive tasks, making it difficult to maintain schedule compliance and long-term maintenance discipline.
Limited Resource Availability
Shortages of skilled technicians, spare parts, or specialized tools can delay scheduled maintenance. Without accurate visibility into resource availability, schedules become unrealistic, leading to incomplete work orders and repeated rescheduling.
Poor Data Quality and Lack of Asset Visibility
Inaccurate asset data, incomplete maintenance histories, or outdated records make it difficult to plan effective schedules. Without reliable data on equipment condition, task durations, or failure patterns, maintenance schedules are often based on assumptions rather than facts.
Manual and Spreadsheet-Based Scheduling
Relying on spreadsheets or manual methods increases the risk of errors, miscommunication, and missed deadlines. These approaches lack real-time updates and make it difficult to adjust schedules quickly when priorities change or emergencies arise.
Inadequate Coordination Across Teams
Maintenance scheduling requires close collaboration between maintenance, operations, and inventory teams. Poor communication can result in scheduling conflicts, unavailable resources, or work being planned during critical production periods.
Skill Mismatches and Workforce Constraints
Assigning tasks without considering technician skills or certifications leads to delays, rework, and safety risks. A lack of structured skill tracking makes it harder to allocate the right people to the right jobs at the right time.
Low Schedule Compliance
Even well-designed schedules can fail if they are not followed. Frequent deviations, skipped preventive tasks, or incomplete work orders reduce the effectiveness of maintenance scheduling and weaken trust in the process.
Resistance to Process Change
Maintenance teams accustomed to reactive workflows may resist structured scheduling practices. Without proper training, communication, and leadership support, new scheduling processes can struggle to gain adoption.
Difficulty Balancing Flexibility and Control
Maintenance schedules must be flexible enough to handle emergencies but structured enough to ensure preventive work is completed. Striking this balance is challenging and often leads to either overly rigid schedules or constant last-minute changes.
Addressing these challenges requires a combination of clear processes, accurate data, cross-functional collaboration, and the right digital tools to support effective and resilient maintenance scheduling.
15 Best Practices of Maintenance Scheduling
Effective maintenance scheduling is not about reacting to breakdowns—it is about preventing failures, optimizing resources, and maintaining operational continuity. When supported by structured processes and MRP software, maintenance teams can plan work more accurately, reduce downtime, and align maintenance activities with broader operational goals.
1. Prioritize Assets Based on Criticality
Not all equipment has the same impact on operations, safety, or costs. Maintenance schedules should focus first on assets whose failure could halt production or create safety risks. Using asset criticality analysis, teams can rank equipment based on risk, downtime impact, and repair complexity. This ensures that limited maintenance resources are directed toward the assets that matter most.
2. Ensure Accurate Resource Allocation and Availability
A maintenance schedule is only effective if the required resources are available. This includes technician availability, skills, spare parts, and specialized tools. Accurate capacity planning and resource leveling help prevent overloading teams or leaving resources idle. By assessing workloads against available resources, organizations can create realistic schedules that are achievable and efficient.
3. Align Maintenance Schedules with Production Plans
Maintenance activities must be coordinated with production to avoid unnecessary disruptions. Aligning schedules with production plans allows teams to perform maintenance during planned downtimes, shutdowns, or low-demand periods. This approach minimizes conflicts between maintenance and operations, protects output targets, and ensures that essential maintenance work does not negatively impact customer commitments.
4. Conduct Regular Inspections and Equipment Monitoring
Regular inspections provide early visibility into equipment condition and performance. When combined with monitoring data, inspections help identify potential issues before they escalate into failures. This information supports condition-based and predictive maintenance, enabling teams to schedule work at the most appropriate time. As a result, maintenance becomes more proactive, targeted, and cost-effective.
5. Move from Reactive to Preventive Maintenance
Reactive maintenance leads to frequent emergencies, higher costs, and shortened asset life. Preventive maintenance focuses on scheduled inspections and servicing based on manufacturer guidelines and historical data. By addressing wear and minor issues early, organizations reduce unexpected breakdowns, stabilize maintenance workloads, and significantly extend the operational lifespan of critical equipment.
6. Standardize Maintenance Tasks, Frequencies, and SOPs
Standardization brings consistency and clarity to maintenance scheduling. Creating repeatable job plans, defined task frequencies, and clear scheduling SOPs ensures that maintenance activities are executed uniformly across teams and locations. This reduces errors, improves training efficiency, and makes schedules easier to manage, replicate, and improve over time.
7. Assign the Right Technicians Using a Skills Matrix
Effective scheduling depends on matching tasks with the right skills. Maintaining an updated skills and certification matrix allows schedulers to assign work to qualified technicians. This improves job quality, reduces rework and safety risks, and balances workloads more effectively. Over time, it also helps identify skill gaps and training needs.
8. Schedule Close to 100% of Available Labor Capacity
Under-scheduling labor often leads to inefficiencies and wasted time. Best-performing maintenance teams aim to schedule close to full available labor capacity, then adjust as needed. This approach increases productivity while still allowing flexibility for urgent work. Gradually increasing scheduled capacity helps teams adapt without overwhelming technicians.
9. Ensure Spare Parts and MRO Availability
Maintenance work cannot proceed without the right parts. Scheduling should be closely coordinated with MRO and inventory planning to ensure spare parts are available before work begins. This prevents delays, avoids repeated rescheduling, and reduces equipment downtime. Strong alignment between maintenance and inventory teams is critical for schedule reliability.
10. Layer Maintenance Tasks During Planned Downtime
Layering maintenance tasks improves efficiency by reducing the number of equipment shutdowns. By combining weekly, monthly, and annual tasks during planned downtimes or shutdowns, teams can maximize maintenance windows. This approach minimizes production interruptions and ensures that multiple maintenance activities are completed in a single, coordinated effort.
11. Develop a Structured Process for Emergency Work
Unexpected breakdowns will occur, even with strong preventive practices. A structured process for emergency work ensures urgent tasks are identified, prioritized, and assigned quickly. Clear escalation paths and predefined roles prevent confusion and help teams respond effectively, without completely derailing planned maintenance schedules.
12. Optimize Communication Across Teams
Maintenance scheduling relies on clear communication between maintenance, operations, and inventory teams. Regular schedule reviews, shared visibility into work orders, and real-time updates reduce misunderstandings and conflicts. Open communication ensures that everyone understands priorities, constraints, and changes, leading to smoother execution and fewer last-minute disruptions.
13. Leverage MRP Software for Maintenance Scheduling
Manual scheduling often leads to errors and missed deadlines. MRP software centralizes maintenance schedules, work orders, resource availability, and inventory data in one system. Automated scheduling, real-time updates, and integrated planning help teams respond quickly to changes while maintaining control and visibility across maintenance operations.
14. Establish Clear Maintenance Goals and KPIs
Clear goals and KPIs provide direction and accountability for maintenance scheduling. Metrics such as schedule compliance, preventive maintenance completion rates, MTBF, MTTR, and equipment uptime help teams evaluate effectiveness. Tracking these KPIs enables data-driven decisions and continuous refinement of scheduling practices.
15. Review, Optimize, and Improve Using Historical Data
Maintenance scheduling should continuously evolve based on past performance. Analyzing historical maintenance data reveals patterns related to failures, workloads, and seasonal trends. These insights help improve forecasting, optimize task frequencies, and enhance schedule accuracy, ensuring maintenance efforts remain aligned with operational needs over time.
How Deskera MRP Helps You with Maintenance Scheduling
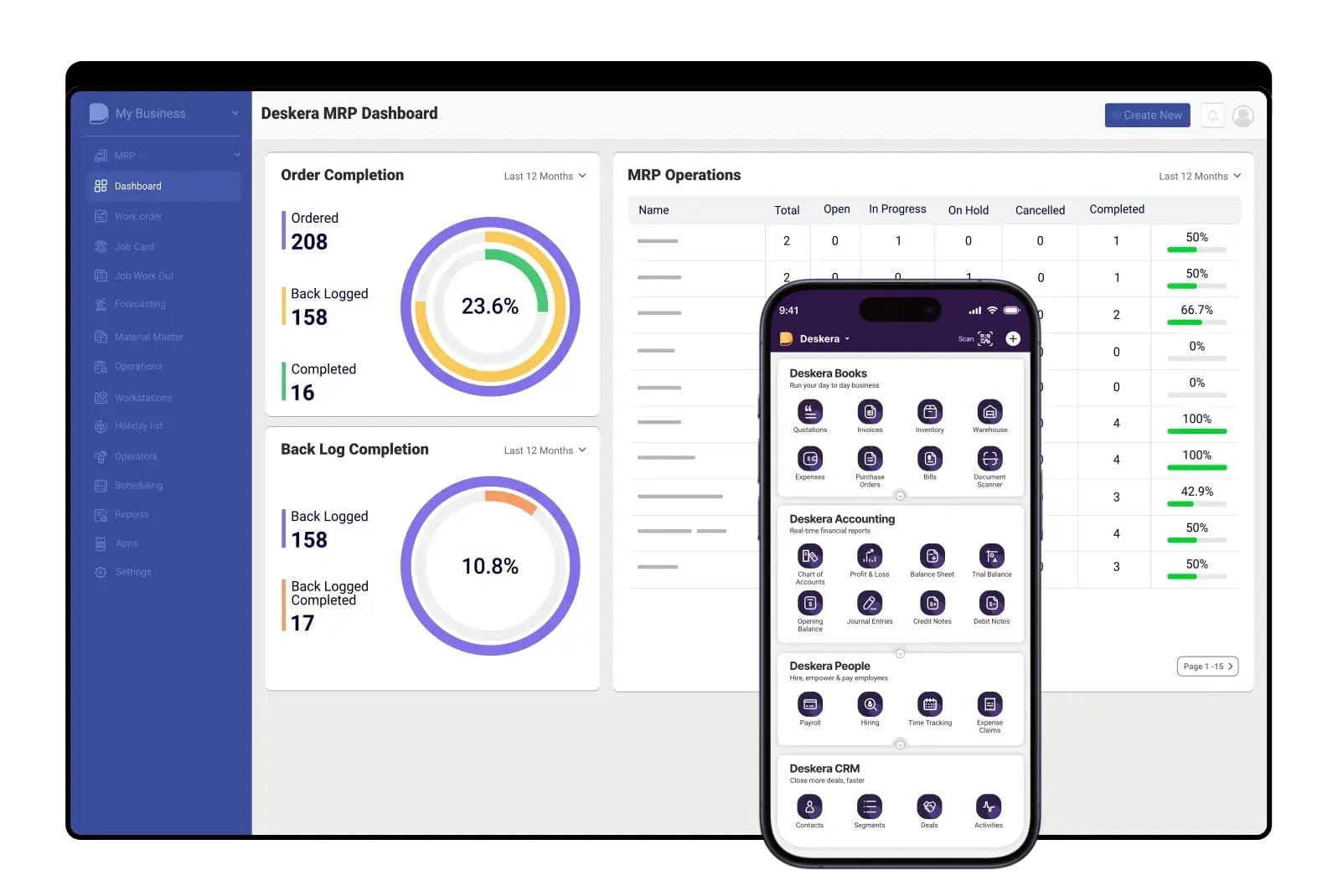
Deskera MRP enables organizations to move from reactive maintenance to structured, data-driven maintenance scheduling by connecting maintenance activities with production, inventory, and resource planning. Instead of managing schedules in isolation, maintenance teams gain a unified view of assets, work orders, and materials, allowing them to plan maintenance with greater accuracy and control.
Centralized Maintenance Planning and Scheduling
Deskera MRP provides a centralized system to plan and schedule maintenance tasks across assets and facilities. Maintenance teams can create preventive maintenance schedules, assign tasks, and track execution from a single platform. This reduces reliance on spreadsheets and ensures schedules are consistent, visible, and easy to adjust when priorities change.
Alignment with Production and Manufacturing Plans
One of Deskera MRP’s key strengths is its ability to align maintenance schedules with production plans. By integrating maintenance activities with manufacturing workflows, teams can schedule maintenance during planned downtimes or low-production periods. This minimizes disruptions while ensuring critical assets receive timely maintenance.
Improved Spare Parts and MRO Coordination
Deskera MRP links maintenance schedules with inventory and MRO data, helping ensure spare parts are available when maintenance is due. This prevents work order delays caused by missing components and reduces excess inventory by aligning part consumption with planned maintenance activities.
Better Resource and Workforce Utilization
With visibility into workloads and task requirements, Deskera MRP helps maintenance teams allocate labor more effectively. Schedulers can plan tasks based on technician availability and required skills, balance workloads across shifts, and reduce overtime caused by last-minute maintenance work.
Data-Driven Preventive Maintenance
Deskera MRP supports preventive maintenance planning by maintaining historical maintenance records and asset data. Teams can use this information to define maintenance frequencies, refine schedules, and shift away from reactive repairs. Over time, this leads to improved asset reliability and longer equipment lifespans.
Real-Time Visibility and Schedule Control
Maintenance schedules are rarely static. Deskera MRP provides real-time visibility into work order status, allowing teams to monitor progress and make informed adjustments when breakdowns or urgent tasks arise. This flexibility helps maintain schedule discipline without sacrificing responsiveness.
Improved Reporting and Performance Tracking
Deskera MRP enables organizations to track maintenance performance through reports and operational data. By monitoring schedule adherence, work order completion, and maintenance trends, teams can continuously improve scheduling accuracy and effectiveness.
By integrating maintenance scheduling with production planning, inventory management, and resource allocation, Deskera MRP helps organizations create reliable, efficient, and adaptable maintenance schedules that support long-term operational performance.
Key Takeaways
- Maintenance scheduling is the structured process of organizing maintenance tasks, resources, and timelines to keep equipment reliable and operations running smoothly.
- Effective maintenance scheduling matters because it reduces operational risk, protects production continuity, and enables predictable maintenance execution aligned with business goals.
- Maintenance planning and maintenance scheduling serve different purposes—planning defines what needs to be done and how, while scheduling ensures the work is executed at the right time with the right resources.
- Following maintenance scheduling best practices helps organizations shift from reactive firefighting to proactive, data-driven maintenance that improves reliability and resource utilization.
- The benefits of maintenance scheduling are measurable and operational, including higher productivity, reduced downtime, improved safety, streamlined workflows, and lower maintenance costs.
- Common maintenance scheduling challenges often stem from resource constraints, poor data visibility, unplanned breakdowns, and lack of coordination between maintenance and production teams.
- Deskera MRP supports effective maintenance scheduling by integrating maintenance activities with production planning, inventory management, and resource visibility, enabling more accurate, flexible, and reliable schedules.
Related Articles