Gross profit margin is also known as gross margin. It is a financial metric which indicates how efficient a company is at managing its operations. Gross profit Margin is a ratio which indicates the performance of a business's sales based on the efficiency of its production process.
Gross profit margin is a valuable financial measurement to business owners and managers as well as to company creditors and investors since it indicates the efficiency with which the company can sell and produce one or more products before extraneous costs are deducted. The gross profit margin is based on the business's (COGS) cost of goods sold. It can be compared to the net profit margin and operating profit margin depending on the information needed. Like other financial ratios, it is the only valuable if the inputs into the equation are correct.

What Is Gross Profit Margin?
Gross profit margin is the financial ratio that business owners or managers use to assess the efficiency of the production process for a product sold by the business or for more than one product. Gross profit is called gross income, gross profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from revenue. Gross profit only include variable costs and does not account for its fixed costs. Gross profit assesses a business's efficiency at using its supplies and labour in producing goods or services.
A company may be more efficient at selling and producing one product than the another. The gross profit margin can be calculated for each of the individual product as long as the company can differentiate the direct costs of producing each product from the others.
The cost of goods sold or COGS on a company's income statement accounts for the direct costs of producing their own products. Direct costs include costs that are specifically tied to a cost object, which may be a product, department, or project.
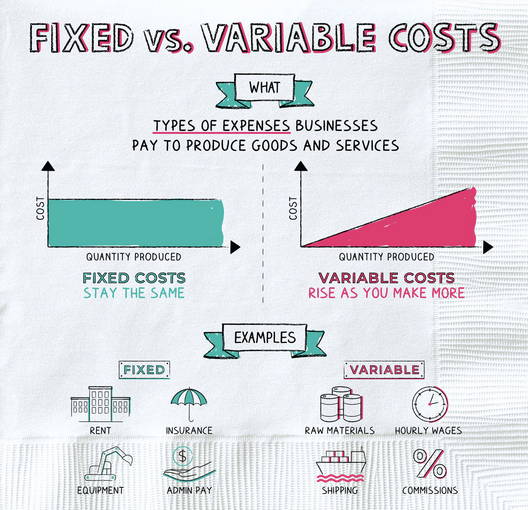
Gross profit does not include fixed costs. Fixed cost is the cost that needs to be paid regardless of the level of output. Fixed costs include insurance, rent, advertising, salaries for employees not directly involved in the production and office supplies.
The other expenses are also known as “fixed costs”. Fixed costs are costs that don’t change or that can change very little, over time. Fixed costs include:
- Rent
- Advertising
- Property Taxes
- Amortization
- Depreciation
- Dues
- Equipment leases
- Insurance
- Interest charges on loans
- Staff salaries
- Subscriptions
- Utilities
Understanding Gross Profit
Gross profit assesses a company's efficiency at using its supplies and labor supplies in producing services or goods. This metric mostly considers variable costs—that is, costs that fluctuate with the level of output, such as:
- Shipping
- Materials
- Direct labor
- Commissions for sales staff
- Credit card fees on customer purchases
- Equipment, perhaps including usage-based depreciation
- Utilities for the production site
For example, if an industrial factory produces 10,000 widgets in a given period, and the company pays $60,000 in rent for the building, a cost of $6 would be attributed to each widget under absorption costing.
Gross profit should not be confused with operating profit. Operating profit is also known as earnings before interest and tax (EBIT), which is a business's profit before taxes and interests are factored in. The operating profit is calculated by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit.

What are the Different Types of Profit Margins?
The three major types of profit are gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin. All of which can be found on the income statement. Each profit type gives analysts more information about a company's performance, especially when it is compared to other competitors and time periods.
Gross Profit Margin
The first level of profitability is gross profit, which is sales minus the cost of goods sold. The calculation of Gross Profit margin is from gross profit. The formula to calculate gross profit margin as a percentage is Gross Margin. It is as per the formula mentioned below:
Gross profit = Total Revenue − Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Gross Margin = (Total Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold)/Total Revenue x 100
For example, if Company X has $100,000 in sales and a COGS of $70,000, it means the gross profit is $30,000, or $100,000 minus $70,000. Divide gross profit by net sales for the gross profit margin, which is 30%, or $30,000 divided by $100,000.
Operating Profit Margin
The second level of profitability is operating profit, which is calculated by deducting operating expenses from gross profit. These are things like selling, general, and administrative costs (SG&A). Operating margin is an important measure of a company's overall profitability from operations. It is the ratio of operating profits to revenues for a company or business segment.Higher ratios are generally better, illustrating the company is efficient in its operations and is good at turning sales into profits.
Operating Profit = Gross Profit − Operating Expenses
Operating Profit = Operating Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold ( COGS) - Operating Expenses - Depreciation - Amortization
Operating Profit Margin = Total Revenue / Operating Profit
Gross profit looks at profitability after direct expenses, and operating profit looks at profitability after operating expenses. If Company X has $10,000 in operating expenses, the operating profit is $30,000 minus $10,000, equaling $20,000. Divide operating profit by sales for the operating profit margin, which is 20%.
Net Profit Margin
The third level of profitably is net profit, which is the income left over after all expenses, including taxes and interest - have been paid. The net profit margin, or simply net margin, measures how much net income or profit is generated as a percentage of revenue. It is the ratio of net profits to revenues for a company or business segment.
Net Profit or Net Income = Operating Profit − Taxes & Interest
Net Income or Net Profit = Revenue − Cost of Goods Sold − Operating Expenses − Other Expenses − Interest − Taxes
Net Profit Margin = Net Profit/ Revenue
Net profit is calculated by deducting both taxes and interest, of these from operating profit. In the example of Company X, the answer is $20,000 minus $10,000, which equals $10,000. Divide the net profit by sales for the net profit margin, which is 10%.
What is the Difference Between Net Profit and Gross Profit?
The gross profit refers to subtracting the variable costs, or cost of goods sold (COGS) from its sales, net profit further subtracts interest costs and taxes from company earnings.
Net profit is also referred to as the “bottom line” since it falls on the last line of a business's income sheet. It is usually used to measure the profitability of a business.
Gross profit refers to a company's profits earned after subtracting the costs of producing and distributing its products. The gross profit assesses a company's ability to earn a profit while simultaneously managing its production and labor costs.
Net income or net profit indicates a company's profit after all of its expenses have been deducted from revenues. The net profit is an all-inclusive metric for profitability and provides insight into how well the management team runs all aspects of the company or business. The net profit is often referred to as the "bottom line" due to its positioning at the bottom of the income statement.
Gross profit is an important metric in determining if and why a company's profits increase or decrease by looking at sales, labor costs, production costs and productivity. For example, if a business reports an increase in revenue, but it is more than offset by an increase in production costs, such as labor, the gross profit will be lower for that period. Let us look at an example.
If a company is hired for a too few production workers for its busy season, it would lead to more overtime pay for its existing workers. The result would be higher labor costs and an erosion of gross profitability.

Using gross profit as an overall profitability metric would be incomplete and unfair since it does not include all of the other costs involved in running a successful company and business.
Meanwhile, net profit represents the profit from all aspects of a company's business operations. As a result, net income or net profit is more inclusive than gross profit and can provide insight into the management team's effectiveness.
For example, a business might increase its gross profit while simultaneously mishandling its debt by borrowing too much. The additional interest expense for servicing the debt could reduce net income despite the business's successful sales and production efforts.
Gross profit can have its limitations since it does not apply to all businesses, companies and industries. For example, services company would not likely have production costs nor costs of goods sold.
Even though net income is the most complete measurement of a business's profit, it too has its limitations and can be misleading. For example, if a business sold a building, the money from the sale of the asset would increase net income for that period. Creditors and investors looking only at net income can misinterpret the company's profitability as an increase in the sale of its services and goods.
How is Gross Profit calculated?
The formula for gross profit is as follows:
Gross Profit = Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold
Revenue - This is the amount of money generated from the sale of a product during a specific time period. The amount is before any deductions.
Cost of Goods Sold - Cost of Goods Sold (or COGS) are direct costs associated with producing a product. They include:
- Depreciation
- Factory overhead
- Labor
- Materials
- Storage
COGS does not include administrative or marketing charges.
Let’s use an example of a company calculating its gross profit.
Bell’s Glasses is a manufacturer of high-end sunglasses. The company is headquartered in California. Bell's glasses are shipped all over Boston to a variety of stores. The company has been in business for one year, and now that she’s doing the year end finances, Bell wants to calculate her gross profit.
Bell first determines the company’s revenue. This is the amount of money her company has made, without any deductions like how much it costs to make the sunglasses to be $950,000.
Bell then looks at calculating her COGS, or cost of goods sold. This includes all the material she needs to buy in order to make the sunglasses, as well as the labor to make them.
There are other cost considerations too. COGS for Bell’s Glasses for the year turns out to be $650,000.
Bell knows the formula for Gross Profit is:
Gross Profit = Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold
Or, in her case:
Gross Profit = $950,000 – $650,000 = $300,000
Bell's Glasses has realized a gross profit of 300k.
Gross Profit Margin is also known as “gross margin” is simply gross profit, expressed as a percentage.
Gross Profit Margin = (Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold)/Revenue x 100
In the case of Bell’s Glasses, the calculation would be:
Gross Profit Margin = ($850,000 – $650,000)/$850,000 x 100 =24% margin
The gross profit margin for Bell's Glasses is 24%. To recap, this is the percentage of revenues that remain after deducting COGS.
Which Financial Report Shows the Gross Profit?
Gross profit will appear on a business's income statement and can be calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from the revenue (sales). These figures can be found on a company's income statement. Gross profit may also be referred to as sales profit or gross income.
The easiest way to calculate your Gross Profit Margins is by using accounting software for invoicing and sales management.
While the number can be calculated manually, using accounting software's such as Deskera Books helps track revenue and expenses accurately, providing you with the gross profit margin figure that you can trust.
Key Takeaways
- Gross profit includes variable costs but does not account for fixed costs
- Gross profit calculates a business's efficiency at using its labor and supplies in producing goods or services.
- Gross profit refers to a business's profits earned after subtracting the costs of producing and distributing its products.
- Gross profit assesses a business's ability to earn a profit while simultaneously managing its production and labor costs
- A gross profit margin is the percentage of revenue generated that's greater than the COGS. To calculate gross profit margin, divide gross profit by revenue and multiply the result by 100.
- Gross profit is the fixed dollar amount, while gross margin is a ratio.
- Both measure a company's profitability using its revenue and cost of goods sold (COGS)








