Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are powerful tools that help organizations streamline operations, integrate processes, and make data-driven decisions. Yet, implementing an ERP system successfully remains one of the biggest challenges for businesses. Studies reveal that around 64% of ERP projects exceed their budgets, often due to underestimated staffing needs or scope creep. This shows that implementation is not just about deploying software—it requires careful planning and structured execution.
Time is another critical factor. While nearly 49% of ERP projects go live on schedule, about 27% experience delays, sometimes pushing back operational improvements by months. These delays can cascade into cost overruns and organizational frustration, making it essential for businesses to follow a disciplined implementation process. Without a roadmap, companies risk wasting resources and eroding confidence in the system.
Even after deployment, the challenge of adoption remains. Research highlights that only 26% of employees fully utilize their ERP systems, leading to underperformance and missed ROI. This gap often stems from insufficient training, weak change management, or overly complex system design. To overcome these hurdles, many organizations rely on a phased ERP implementation approach, adopted by 58.5% of companies, as it allows gradual integration, testing, and user adaptation.
Nearly two-thirds of ERP projects face budget overruns, but a structured, phased approach can transform ERP into a catalyst for business growth.
This is where solutions like Deskera ERP stand out. Built for modern businesses, Deskera offers cloud-based ERP with pre-configured templates, easy customization, and mobile accessibility. Its AI-powered assistant, David, helps simplify complex tasks, while its scalable design supports companies at every stage of growth. By following structured implementation phases and leveraging intelligent platforms like Deskera ERP, organizations can minimize risks, control costs, and achieve long-term success.
What is ERP Implementation?
ERP implementation is the process of adopting and integrating an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system into a business’s daily operations. An ERP system is a comprehensive solution that centralizes data and automates critical functions such as finance, human resources, sales, supply chain, and manufacturing. By bringing these functions together, ERP systems help organizations improve efficiency, reduce manual errors, and make informed decisions faster.
ERP implementation isn’t just a software upgrade—it’s a business transformation that reshapes processes and people.
The implementation process typically involves planning, configuring, and deploying the ERP system, which can take several months depending on the scope and complexity of the organization. Unlike installing simple software, ERP implementation is more of a business transformation initiative, as it requires redesigning processes to fully leverage the system’s capabilities. This means aligning the software with business goals, customizing it to fit unique workflows, and ensuring the new processes are optimized for efficiency.
A successful implementation involves multiple phases: requirement gathering, system configuration, data migration, testing, user training, and post-deployment support. Each step has its own set of challenges, making careful planning and a structured, phased approach essential. For instance, without proper data migration strategies or user acceptance testing, businesses risk running into delays, budget overruns, or poor adoption rates.
It’s important to note that ERP implementation is not just a technical project—it is change management at its core. Securing leadership support, building cross-department collaboration, and investing in early training are vital to preparing employees for the transition.
Open communication and incorporating employee feedback can also make adoption smoother. In essence, ERP implementation is about more than installing software; it’s about transforming how a business operates to achieve long-term growth and efficiency.
ERP Implementation Phases
ERP implementation is not a one-time activity—it’s a structured journey that unfolds through distinct phases. While the number of phases may vary depending on methodology and organizational needs, most ERP projects follow a six-to-eight stage process that ensures alignment between business goals, system capabilities, and user adoption. Each phase builds upon the previous one, making it critical to approach the lifecycle with patience, planning, and precision.
Breaking ERP into phases is like building a house—you need a strong foundation before adding walls and finishing touches.
Below are the key phases of ERP implementation that organizations should understand and execute carefully:
1. Pre-Implementation & Planning
The planning phase sets the foundation for ERP success. Here, organizations assess current processes, identify gaps, and define the objectives they aim to achieve with ERP. A dedicated project team is established, including leadership, IT, and end-user representatives. Together, they set budgets, timelines, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
This phase also involves creating a clear business case and roadmap to ensure alignment with long-term strategy. By carefully preparing at this stage, businesses minimize risks and establish clear expectations, ensuring that the ERP journey is structured, focused, and more likely to succeed.
2. Vendor Selection
Choosing the right ERP vendor is critical to the project’s outcome. Businesses evaluate ERP systems based on scalability, deployment options (cloud vs. on-premises), integration capabilities, and ease of use. Cost transparency, industry-specific features, and vendor support also play significant roles.
Typically, companies request product demonstrations and issue Requests for Proposals (RFPs) to compare solutions. A careful selection ensures the chosen ERP aligns with business goals and can evolve with growth. By selecting a vendor that offers flexibility, proven experience, and ongoing support, organizations can secure a strong partner for their ERP journey and long-term digital transformation.
Choosing the right ERP vendor isn’t about features alone—it’s about finding a partner who understands your business journey.
3. System Design & Customization
In this phase, the ERP system is tailored to fit the organization’s needs. It begins with mapping business processes and aligning them with ERP functionalities. Workflows are redesigned for efficiency, while configurations are set for roles, permissions, and reporting. Although customization is possible, companies are encouraged to prioritize standardization to avoid complexity and unnecessary costs.
Striking the right balance ensures flexibility without compromising stability. Involving end-users in the design process enhances practicality and adoption. This stage is crucial to building an ERP system that not only meets technical requirements but also supports real-world operations seamlessly.
4. Data Migration
Data migration is one of the most critical yet challenging ERP phases. Businesses must determine which data to transfer, clean outdated or duplicate records, and standardize formats for consistency. The process includes extracting data from legacy systems, transforming it to fit the new ERP structure, and loading it into the new platform.
To avoid errors, migration is often conducted in stages with thorough testing at each step. Accurate, clean data ensures the ERP delivers reliable insights and smooth operations from day one. A structured migration strategy prevents costly mistakes and protects business continuity during implementation.
5. Testing
Before the ERP system goes live, comprehensive testing ensures it functions correctly and supports day-to-day business needs. Testing typically includes unit testing for individual modules, integration testing for cross-functional workflows, performance testing under real conditions, and User Acceptance Testing (UAT).
UAT is particularly important because it involves employees verifying that the system supports their responsibilities. Testing helps identify gaps, bugs, or inefficiencies before launch, reducing risks of disruption. A rigorous testing process ensures the ERP is not only technically sound but also aligned with business operations, providing confidence for a smooth go-live transition.
The best ERP systems are not built in design rooms—they’re refined through rigorous testing with real users.
6. Training & Change Management
ERP success depends heavily on user adoption, making training and change management vital. Training programs are designed for different roles, ensuring employees understand how to use the system in their daily tasks. Change management strategies include clear communication about benefits, addressing resistance, and involving employees early in the process.
Organizations may also appoint “change champions” within departments to guide peers. Preparing staff reduces anxiety and builds confidence in the system. When employees feel supported and knowledgeable, adoption rates increase significantly, ensuring the ERP investment delivers measurable improvements in productivity and efficiency.
An ERP system is only as powerful as the people who use it—training turns resistance into adoption.
7. Go-Live
Go-live isn’t the finish line; it’s the starting point of continuous improvement.
Go-live marks the official transition from legacy systems to the new ERP platform. Companies may choose a “big bang” rollout, where the entire system is launched at once, or a phased rollout, deploying modules gradually. Regardless of the method, this stage requires careful coordination, with IT teams and vendors on standby to address issues quickly.
Some organizations run parallel systems temporarily to minimize risks. The success of go-live depends on preparation in earlier phases—especially testing and training. A well-executed go-live ensures minimal disruptions and enables the business to start reaping ERP benefits immediately.
8. Post-Implementation Support & Optimization
The ERP journey doesn’t end at go-live. Post-implementation involves continuous monitoring, troubleshooting, and collecting user feedback. Regular updates, security patches, and performance evaluations keep the system reliable and secure. Organizations also use this phase to refine workflows, optimize processes, and add new modules as business needs evolve.
Ongoing training and support ensure employees remain confident in using the system. Long-term success requires ERP optimization to adapt to growth and market changes. By treating implementation as an ongoing journey, companies maximize ERP value and maintain a system that grows alongside their strategic objectives.
By following these phases diligently, businesses can reduce risks of budget overruns, project delays, and poor user adoption—turning ERP implementation into a transformative success rather than a costly challenge.
Case Studies for Each Phase of ERP Implementation
In this compilation of case studies, we explore how organizations can successfully navigate each stage of ERP implementation. While the examples use fictional company names, they provide real-world insights into the challenges faced, strategies adopted, and outcomes achieved. Mid-size companies can use these lessons to optimize ERP adoption, enhance collaboration, and drive digital transformation success.
1. Pre-Implementation Phase: MNO Consulting
ERP success begins long before the software arrives; it starts with alignment, planning, and shared vision.
MNO Consulting, a mid-sized professional services firm with offices in three countries, faced skepticism from department heads about ERP adoption. They launched workshops and Q&A sessions to explain how ERP would improve collaboration and client delivery.
By addressing concerns transparently and highlighting business value, they secured alignment from leadership and staff. This early buy-in ensured that all stakeholders worked toward a shared vision, creating a strong foundation for the project.
2. Vendor Selection Phase: PQR Manufacturing
PQR Manufacturing, a growing automotive parts producer, needed an ERP vendor that could handle complex supply chain requirements. They built a cross-functional evaluation team and ran pilot demos with shortlisted vendors.
After analyzing functionality, support services, and cost, they selected a vendor with proven industry expertise and ISO-27001 compliance. The rigorous process minimized risks and ensured their ERP could scale with business expansion.
3. Planning and Preparation Phase: LMN Solutions
LMN Solutions, an IT services company, struggled with coordinating its global implementation team. To address this, they appointed an experienced ERP project manager to oversee the initiative.
The manager introduced a phased project plan, set up weekly progress reviews, and ensured responsibilities were clearly defined. This structured planning helped LMN mitigate risks, keep everyone accountable, and adapt flexibly to challenges without missing deadlines.
4. Customization and Configuration Phase: RST E-Commerce
RST E-Commerce, a global online retailer, faced the challenge of handling regional payment systems and regulatory requirements. They opted for a “core standardization + limited customization” approach.
The ERP system was standardized for inventory, customer management, and reporting but customized for local tax rules and diverse payment gateways. This balance reduced complexity, improved efficiency, and allowed RST to expand globally without sacrificing compliance.
5. Data Migration Phase: GHI Textiles
GHI Textiles, a mid-size apparel manufacturer, initially planned to migrate all historical data from its legacy systems. However, after a data audit, they discovered many inactive supplier accounts and outdated sales records.
Instead of migrating everything, they prioritized relevant and accurate data. By cleaning and standardizing information before migration, they reduced errors, improved reporting accuracy, and saved significant implementation time and costs.
6. Testing Phase: UVW Logistics
UVW Logistics, a shipping and warehousing company, made testing central to its ERP journey. They designed simulations of real-world logistics operations, including delayed shipments and customs bottlenecks.
Employees from different departments participated actively, giving feedback that led to key refinements. This thorough testing phase ensured a smooth go-live and eliminated disruptions that could have delayed client deliveries.
7. Training and Change Management Phase: OPQ Travel
OPQ Travel, an international travel agency, recognized the importance of training to drive user adoption. They conducted multilingual training sessions tailored to different roles, such as finance teams, booking agents, and customer service staff.
To ease the transition, they appointed “change ambassadors” in each office to provide on-the-ground guidance. This strategy fostered confidence, minimized resistance, and ensured employees fully utilized the system.
8. Go-Live and Post-Implementation Phase: DEF Healthcare
DEF Healthcare, a regional healthcare services provider, ensured a smooth go-live by setting up a 24/7 support desk for the first 60 days. They created a ticketing system to track issues and assigned dedicated staff to resolve them quickly.
Post-go-live, they scheduled feedback sessions with doctors, nurses, and administrators to optimize workflows. The proactive support approach reduced downtime, boosted adoption, and enhanced patient care delivery.
Importance of ERP Implementation Phases
ERP implementation is a complex journey that touches every aspect of an organization. Breaking it down into structured phases ensures that the transition is smooth, controlled, and aligned with business objectives.
Each phase plays a vital role in reducing risks, managing costs, and driving successful adoption. By understanding the importance of each stage, companies can maximize the return on their ERP investment while minimizing disruptions.
1. Provides Structure and Clarity
Phased implementation brings order to a complex process. Instead of tackling everything at once, businesses move step by step—planning, configuring, testing, and training. This structured approach clarifies roles, responsibilities, and deliverables, reducing confusion and ensuring the entire project stays aligned with business goals.
2. Reduces Risk of Failure
Implementing ERP without phases can overwhelm resources and increase the chances of costly errors. By breaking the project into smaller milestones, risks are identified and addressed early. This proactive approach prevents major failures during go-live and ensures smoother system adoption.
3. Improves Data Accuracy and Quality
Data migration and testing are critical ERP phases. Without them, businesses risk inaccurate, duplicate, or missing data in their new system. The phased approach ensures data is cleansed, validated, and tested, leading to more reliable insights and operational efficiency.
4. Enhances User Adoption
Phases like training and change management focus on preparing employees for the new system. Instead of overwhelming users with sudden change, phased implementation introduces them gradually. This helps employees adapt, reduces resistance, and encourages effective use of ERP features.
5. Ensures Cost and Time Management
ERP projects are notorious for budget overruns and delays. Phased implementation allows organizations to track progress against set milestones, adjust resources, and avoid scope creep. This level of control makes it easier to manage budgets and timelines effectively.
6. Enables Continuous Improvement
Post-implementation is often overlooked but plays a vital role in ERP success. This phase allows businesses to refine workflows, add new modules, and improve efficiency over time. Treating ERP as an ongoing journey ensures the system remains valuable and evolves with business needs.
This section highlights why following ERP phases is not just a best practice but a necessity for long-term success.
Common Challenges in ERP Implementation Phases
Despite its benefits, ERP implementation is rarely straightforward. The process involves multiple stakeholders, complex workflows, and significant investments of time and resources. Without careful execution, organizations may face pitfalls that impact timelines, budgets, and adoption.
Understanding these common challenges helps businesses anticipate risks and proactively develop strategies to overcome them.
1. Budget Overruns
One of the most frequent issues is exceeding the planned budget. This happens due to underestimated staffing needs, unexpected customization, or scope expansion. Studies show that around 64% of ERP projects face budget overruns, making financial control and proper forecasting critical throughout all phases.
2. Project Delays
ERP projects are complex, often involving multiple departments and processes. Miscommunication, inadequate testing, or resource shortages can cause delays. In fact, 27% of ERP implementations miss their go-live dates, highlighting the importance of strong project management and realistic scheduling.
3. Data Migration Issues
Bad data is the silent killer of ERP projects; clean data is the foundation for accurate decisions.
Migrating data from legacy systems to the new ERP is challenging. Problems such as incomplete, duplicate, or inconsistent data can disrupt operations. Without thorough cleansing, validation, and testing, businesses risk poor insights and inefficiencies after go-live.
4. Resistance to Change
Employees often resist adopting new systems due to fear of change or lack of training. Low adoption rates can significantly reduce the ROI of ERP investments—only 26% of employees fully use their ERP systems. Effective change management and role-specific training are crucial to overcome this hurdle.
5. Over-Customization
While customization may seem attractive, excessive modifications can increase costs, complicate upgrades, and reduce system stability. Many businesses fall into the trap of over-customizing their ERP instead of adapting processes to align with standard system features.
6. Lack of Executive Support
ERP implementation requires buy-in from top management. Without leadership support, projects may lack direction, resources, or authority to drive necessary process changes. Executive involvement ensures accountability and alignment with organizational goals.
7. Inadequate Post-Implementation Support
Many companies mistakenly consider ERP implementation complete after go-live. However, without ongoing monitoring, updates, and user support, systems can quickly become underutilized or outdated. Post-implementation optimization is essential for maximizing long-term value.
By recognizing these challenges, organizations can prepare better strategies, allocate resources effectively, and increase the chances of a smooth, successful ERP implementation.
Best Practices for Successful ERP Implementation
Simply following ERP implementation phases does not guarantee success. Each stage must be supported by proven best practices that strengthen execution, minimize risks, and encourage long-term adoption. ERP projects are large-scale investments of time, money, and resources, so implementing them the right way is critical.
Below are some best practices that can help organizations maximize ERP value and ensure a smoother transition.
1. Invest Time in Thorough Planning
The planning and discovery phase should never be rushed. Strong planning builds the foundation for the entire ERP journey by defining goals, timelines, budgets, and responsibilities. Securing executive sponsorship at this stage ensures alignment with broader business strategies.
Organizations should also anticipate resource needs realistically and prepare contingency plans. By dedicating sufficient time to planning, companies reduce risks of budget overruns, missed deadlines, and misaligned expectations later in the process.
2. Choose the Right ERP System
Selecting the right ERP solution is one of the most critical steps. The chosen system must align with the company’s size, industry, workflows, and long-term growth plans. Businesses should evaluate deployment models (cloud vs. on-premises), scalability, integration capabilities, and ease of use.
Cost considerations and vendor reputation also play a role. Choosing the right ERP from the start minimizes disruptions, avoids expensive customizations, and ensures the solution can grow alongside the organization.
3. Plan Data Migration Carefully
Data migration can make or break ERP success. Many organizations make the mistake of transferring all historical data without assessing its value. Instead, companies should take this opportunity to cleanse, standardize, and rationalize data.
Outdated customer accounts, inactive suppliers, and redundant records should be eliminated. Creating a structured migration strategy ensures accuracy and prevents operational issues post-go-live. Clean, reliable data lays the groundwork for accurate reporting and better decision-making.
4. Prioritize Training and Support
Deployment is not the end of ERP implementation—it is the beginning for users. Effective training ensures employees understand how to use the system in real-world scenarios. Training should be role-specific, practical, and continuous, not just a one-time event.
Organizations should also allocate resources for ongoing support, technical troubleshooting, and system updates. When users feel confident and supported, adoption rates rise, and the ERP system delivers measurable benefits.
5. Emphasize Communication and Change Management
Clear communication throughout the project builds trust and reduces resistance. Employees must understand why the ERP is being implemented, what benefits it will bring, and how it will affect their daily tasks.
Two-way communication is equally important—listening to employee concerns can uncover issues before they escalate. Assigning change champions within departments helps drive adoption and maintain enthusiasm.
Strong communication and change management ensure employees become active participants, not reluctant users.
6. Focus on Continuous Improvement
ERP implementation is not a one-time project but an ongoing journey. After go-live, organizations should continue monitoring performance, optimizing workflows, and gathering feedback.
Adding features gradually, refining processes, and keeping the system updated ensures it continues to meet evolving business needs. Companies that view ERP as a long-term investment—rather than a short-term project—realize higher ROI and greater adaptability to changing market conditions.
By following these best practices, organizations can avoid common pitfalls, accelerate time-to-value, and ensure that ERP becomes a driver of efficiency, collaboration, and growth.
How Deskera ERP Simplifies Implementation
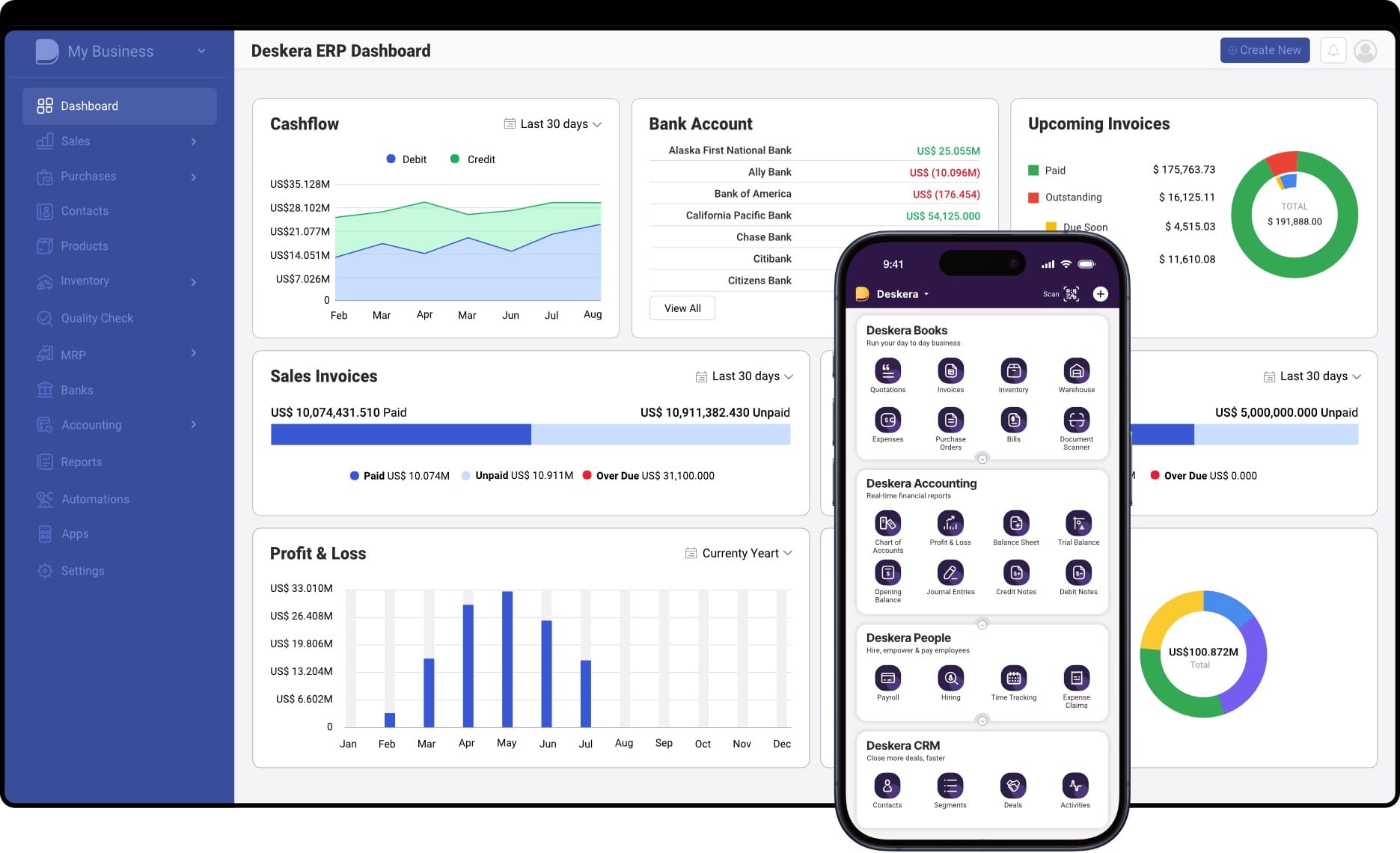
Implementing an ERP system can feel overwhelming, but choosing the right solution makes the process significantly easier. Deskera ERP is designed with small and medium businesses in mind, offering an intuitive, cloud-based platform that simplifies every phase of ERP implementation—from planning to post-go-live optimization. With built-in automation, AI assistance, and user-friendly interfaces, Deskera reduces complexity and accelerates time-to-value.
Here’s how Deskera ERP streamlines implementation:
1. Quick and Flexible Deployment
Deskera’s cloud-based architecture eliminates the need for heavy upfront IT infrastructure and long installation processes. Businesses can go live faster while enjoying the flexibility to scale as they grow. This reduces both implementation costs and delays.
2. Simplified Data Migration
Data migration is one of the most challenging ERP phases, but Deskera simplifies it with easy import tools, templates, and built-in validation features. This ensures clean, accurate data transfer from legacy systems without unnecessary complications.
3. AI-Powered Assistance with David
Deskera’s AI assistant, David, helps guide users through system navigation, reporting, and troubleshooting. By offering real-time insights and support, David reduces the learning curve and empowers employees to adapt to the new system more quickly.
4. Built-In Training and User-Friendly Interface
ERP adoption often fails due to poor training, but Deskera minimizes this risk. Its intuitive design makes it easy for employees to learn and use daily. Additionally, Deskera provides learning resources and onboarding support, helping organizations achieve higher adoption rates.
5. Seamless Integration and Automation
Deskera integrates with core functions like accounting, inventory, sales, and HR, reducing the need for multiple disconnected systems. Its automation features also streamline repetitive tasks such as invoicing, payroll, and reporting, freeing teams to focus on strategic work.
6. Ongoing Support and Scalability
ERP success doesn’t end at go-live, and Deskera ensures continuous support with updates, customer service, and scalability options. Businesses can add modules or expand usage as their needs grow, making Deskera a long-term partner in operational efficiency.
By addressing common ERP pain points such as migration, training, and adoption, Deskera ERP makes implementation smoother and more cost-effective—helping businesses unlock ERP benefits faster without the typical roadblocks.
Deskera ERP simplifies complexity, helping businesses move from planning to performance with speed and confidence.
Key Takeaways
- ERP implementations are high-stakes projects, with challenges like 64% facing budget overruns and 27% experiencing delays. A phased approach—preferred by 58.5% of companies—helps reduce risks, improve adoption, and ensure long-term success. Deskera ERP offers a user-friendly, cloud-based solution that simplifies this journey.
- What is ERP Implementation?: ERP implementation is the structured process of adopting, configuring, and deploying ERP software to integrate business functions. It requires careful planning, process redesign, system customization, testing, and change management to achieve efficiency and productivity gains.
- Phases of ERP Implementation: Breaking ERP implementation into phases—planning, vendor selection, design, data migration, testing, training, go-live, and post-support—provides structure, minimizes risks, and ensures each step builds toward a successful transition.
- Importance of ERP Implementation Phases: A phased approach adds clarity, reduces failure risks, ensures accurate data migration, improves user adoption, helps control costs and timelines, and supports continuous improvement post-go-live.
- Common Challenges in ERP Implementation Phases: Businesses often face hurdles such as budget overruns, project delays, poor data migration, employee resistance, over-customization, lack of executive support, and weak post-go-live strategies—all of which can derail ERP success.
- Best Practices for Successful ERP Implementation: Success depends on thorough planning, choosing the right ERP system, careful data migration, robust training and support, open communication, and ongoing optimization. These practices maximize ROI and sustain long-term value.
- How Deskera ERP Simplifies Implementation: Deskera ERP reduces complexity with quick cloud deployment, easy data migration, AI-powered assistance, intuitive design, seamless integration, and ongoing support—helping businesses avoid common ERP pitfalls and accelerate adoption.
Related Article

















